The hips are highly active joints. Hip sprains are rare but do occur. A hip sprain is caused by tearing or stretching the ligaments that surround the hip and join the bones to each other. This is different from a hip strain, which is an injury to the muscles and is generally caused by over-use of the hip flexor muscles and tendons, causing them to tear. Hip sprains usually happen after a fall or a sudden twisting motion, which can occur during sports or an accident.
Individuals involved in sports that require quick stops, body shifting, and sudden direction changes, like soccer, football, basketball, tennis, volleyball, etc., have an increased risk. Most hip sprains can be effectively treated with conservative treatments like self-massage, rest, ice, and nonsteroid anti-inflammatory medications. For more severe cases, physical therapy and chiropractic can treat the condition.
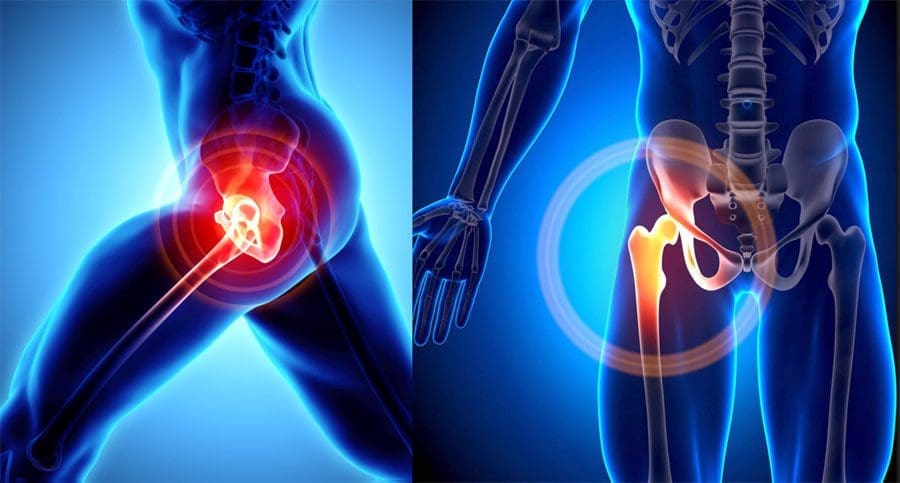
Table of Contents
Hip Sprain Symptoms
- Tenderness in the hip increases when lifting the thigh.
- Cramping sensation/s in the muscles of the upper leg.
- Swelling in the hip or thigh
- Bruising in the hip or thigh.
- Sudden pain in the hip or pelvis.
- Sharp pain in the hip or pelvis.
- Pain that worsens when walking, running, or stretching the hip muscles.
- Loss of strength in the front of the groin.
- Tugging or pulling sensation.
- Limping.
Diagnosis
The doctor or chiropractor will:
- Look into medical history.
- Inquire about symptoms.
- Inquire about activities that could cause symptoms.
- Perform a physical examination.
- Ask the individual to perform a variety of movements to determine what type of injury has been sustained.
- Other conditions could cause radiating pain.
- Pain in one or both hips might not have anything to do with the hips but a pinched nerve root in the lower back.
- Sciatica can develop when certain nerve roots in the lower back are irritated or compressed, causing symptoms to travel down the sciatic nerve and radiate around the pelvis and leg.
- X-rays can help rule out hip stress fractures, which can have similar symptoms.
- MRI or CT scans are used to see if any soft tissue damage has occurred.
Hip Sprain Treatment
- Treatment usually begins with over-the-counter pain medications and anti-inflammatories to reduce swelling and relieve pain.
- Resting the hip will help prevent further damage.
- Applying ice will help prevent tissue damage and reduce swelling.
- It is recommended to use an ice pack several times a day for the first 48 hours after an injury.
- Once the swelling goes down, a chiropractor and physical therapy team will create a personalized treatment plan that includes:
- Adjustments.
- Exercise therapy.
- Posture training.
- Stretching.
- Massage.
Treatment/Rehabilitation Objectives
- Reduce inflammation.
- Relax muscle spasms.
- Strengthen weakened muscles.
- Improve joint mobility.
Individuals will be shown how to prevent the risk of sprains in the future. This includes:
- Avoiding exercising when the body is tired
- Wearing proper footwear and protective equipment
- Warming up properly before exercise/physical activities.
Depending on the severity of the sprain, surgery could be the last resort to repair the ruptured or torn ligaments.
Body Composition
Realistic Goals
Not seeing results after putting in the work through exercise and diet can be frustrating. Setting realistic goals can help when results are not showing.
Realistic Fat Loss
- Do not expect actual fat loss without being in a caloric deficit.
- The body needs to use more energy than the amount of food/energy taken in; otherwise, excess energy/food gets stored, primarily as adipose tissue.
- Total Daily Energy Expenditure or TDEE is necessary to set a realistic caloric deficit to achieve measurable fat loss.
- There are caloric deficit variations, but most doctors, dieticians, trainers, and fitness experts agree that a caloric deficit of around 500 calories a day that equals to about 3,500 calories a week will result in a pound of fat loss per week.
- One pound of fat a week lost might seem slow, but the one pound of fat is a real pound removed.
- The long-term goal is not to fall back into unhealthy habits and develop and maintain new healthy ones.
References
Brantingham JW, Globe GA, Cassa TK, et al. A single-group pretest posttest design using full kinetic chain manipulative therapy with rehabilitation in the treatment of 18 patients with hip osteoarthritis. Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapy 2012; 33(6): 445-57.
Kamali, Fahimeh and Esmaeil Shokri. The effect of two manipulative therapy techniques and their outcome in patients with the sacroiliac joint syndrome. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies. 2012; 16: 29-35.
McMorland G, Suter E, Casha S, du Plessis SJ, Hurlbert RJ. Manipulation or microdiscectomy for sciatica? A prospective randomized clinical study. Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 2010; 33(8): 576-584.
Tibor, Lisa M, and Jon K Sekiya. “Differential diagnosis of pain around the hip joint.” Arthroscopy: the journal of arthroscopic & related surgery: official publication of the Arthroscopy Association of North America and the International Arthroscopy Association vol. 24,12 (2008): 1407-21. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2008.06.019
Wedro, Benjamin. “Hip Pain: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment Information and Diagnosis-eMedicineHealth.” http://www.emedicinehealth.com/hip_pain/article_em.htm.
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information on this blog site is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters and issues that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card