Can understanding the planes of motion help individuals adjust fitness training to maximize fitness for physical and sports performance and reduce the risk of injury?
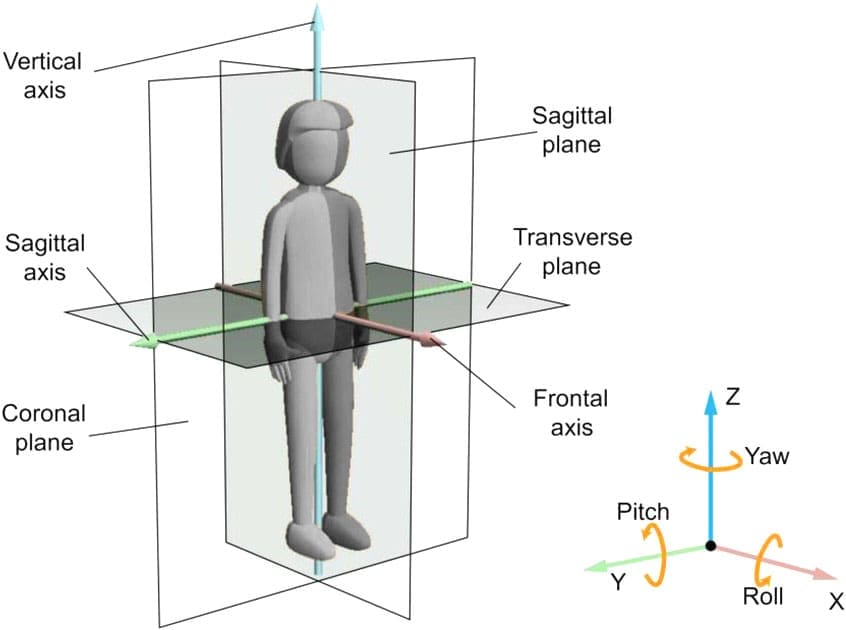
Table of Contents
Planes of Motion
The body’s planes of motion are the sagittal, frontal, and transverse planes, which divide it into left and right, front and back, and top and bottom halves. The body moves in different dimensions during daily work, house chores, and physical activity/exercises. The movements in each plane correspond to forward/backward, side-to-side, and rotational motions. Think of each plane as an imaginary line or a pane of glass that divides the body into opposing segments when standing in the anatomical position. (National Academy of Sports Medicine, 2024)
- Sagittal plane -Divides the body into right and left sides.
- Frontal plane – Divides the body into front and back.
- Transverse plane – Divides the body into top and bottom sections.
To determine the plane of motion of a particular movement, consider how the movement would interact with the imaginary lines or plates. When a movement runs parallel to the imaginary line, the movement is occurring in that plane of motion. For example, when going upstairs, the forward and upward movement at the hip, knee, and ankle occurs primarily in the sagittal plane because that movement runs parallel to the imaginary line that divides the body into right and left sides. Frontal plane movements occur while you walk up the stairs and reach for the handrail. The movement is in the frontal plane because the lateral hand reach runs parallel to the line, dissecting the body into front and back sections. If you turn around to look behind, the rotational movement occurs in the transverse plane because your upper torso runs parallel to the line, dissecting the body into an upper and lower section. Individual movements at any joint in the body can occur in a single plane or multiple planes. Complex movements usually happen in several planes of motion concurrently.
Sagittal Plane
Movement in the sagittal plane generally happens in front or behind. This is the most familiar plane of motion because many typical day-to-day activities happen within arm’s reach in front. Walking, texting, or computer work involves movement primarily in the sagittal plane. Several eating mechanics occur in the sagittal plane. Movements include:
- Flexion – A bending movement that decreases the angle at a joint.
- Extension – An extending movement that increases the angle at a joint.
- Hyperextension – Extending the angle at a joint beyond neutral.
- Dorsiflexion – Bending at the ankle so the top of the foot moves toward the shin.
- Plantarflexion – Pushing the foot down and away from the body.
Many strength-training exercises in the sagittal plane include biceps curls, forward or reverse lunges, squats, vertical jumping, running, downward dog, and yoga chair poses.
Frontal Plane
The frontal plane divides the body into front/anterior and back/posterior sections. Frontal plane movements are lateral or side-to-side and include:
- Abduction – Moving the body or a limb laterally and away from the body’s midline.
- Adduction – Moving the body or a limb towards the body’s midline.
- Elevation – Moving the shoulder blades up.
- Depression – Moving the shoulder blades down.
- Eversion – Rolling the foot towards the inside/medial side.
- Inversion – Rolling the foot towards the outside/lateral side.
Frontal plane movements are less common than sagittal movements. For example, individuals walk forward more than side to side or reach for something in front rather than directly to the side. Frontal plane movements in fitness include side lunges, lateral shoulder raises, and side shuffles, and in yoga poses, standing side bends and the triangle.
Transverse Plane
The transverse plane divides the body into upper/superior and lower/inferior sections. Transverse plane movements generally involve rotation. Movement in this plane is less common. Exercise injuries most often occur during transverse/rotational movements. (National Academy of Sports Medicine, 2024) Movements include:
- Rotation – Moving the torso or a limb around its vertical axis.
- Pronation – Rotating the forearm or foot to a palm-side or foot-side down position.
- Supination – Rotating the forearm or foot to a palm-side or foot-side-up position.
- Horizontal Abduction – Moving the upper arm away from the body’s midline when elevated to 90 degrees.
- Horizontal Adduction – Moving the upper arm towards the body’s midline when elevated to 90 degrees.
Typical everyday activities in the frontal plane include turning the head to look behind or turning a doorknob. Exercises in the transverse plane include hitting a golf ball, swinging a baseball bat, or performing a seated twist.
Training Within the Planes of Motion Benefits
Training in all three planes can help with movement in several ways, providing greater ease in life and sports.
Prepares Body for Daily Tasks
Many traditional strength-training programs focus on training one muscle at a time, often in a single plane of motion. For example, weight lifters might do bicep curls to primarily work the biceps in the sagittal plane, a chest fly exercise to primarily work the pectoral muscles in the transverse plane, or lateral raises to work the shoulders in the frontal plane. However, compound exercises have recently become much more common. Compound movements allow individuals to train several muscle groups simultaneously and in different planes of motion.
In this way, training activities mimic daily living activities. For example, individuals often lift several heavy bags of groceries and turn to open the car or trunk, involving both sagittal and transverse movement. Preparing the body for complex activities with compound exercises allows individuals to perform them more easily throughout the day.
Prepares Body for Sports and Physical Activities
Complex multi-planar movements help prepare for safe and effective physical activity and sports performance (National Academy of Sports Medicine, 2024). Researchers and experts understand that many physical and athletic activities require the body to move in different directions, often quickly and under high stress. Several studies have found that anterior cruciate ligament/ACL injuries are more likely to occur during multi-planar rather than single-planar movements. (Quatman C. E., Quatman-Yates C. C., & Hewett T. E. 2010) Training the body to perform multi-planar movements safely and effectively through exercise can help reduce the risk of injury during daily activities or stressful athletic competitions.
Encourages Variation For Full Body Strengthening
Individuals tend to fall into certain movement patterns, such as repeatedly performing the same fitness activity or exercises. This can cause them to have a favorite plane of motion. One way to break away from the same routine is to include movement from all planes of motion. For example, many abdominal workout machines help train in multiple planes of motion, challenging your body to move in different ways. Dumbbells, kettlebells, TRX straps, and bands allow individuals to move joints freely in various planes of motion and work several muscles.
Runners train primarily in the sagittal plane, even if they cross-train by swimming, cycling, or using cardio machines. For this reason, trainers and coaches often recommend doing some form of yoga or weight training that allows them to move their joints in different ways, including lateral movements or rotation. Even flexibility training should incorporate all three planes of motion. For example, walkers might choose to do a simple calf or hamstring stretch at the end of their workout but may also benefit from a seated spine rotation or a lying hip stretch.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic
Understanding the concept and importance of training in the three planes of motion can help improve sports and physical performance and prevent musculoskeletal injuries. Chiropractic care aims to help individuals enhance movement with less pain due to condition, after injury, or surgery. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to build optimal health and wellness solutions. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, prevent injury, and help mitigate issues through adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal problems.
The Difference of Using Custom Foot Orthotics
References
National Academy of Sports Medicine. (2024). Sagittal, Frontal and Transverse Body Planes: Exercises & Movements. NASM. https://blog.nasm.org/exercise-programming/sagittal-frontal-traverse-planes-explained-with-exercises?utm_source=blog&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=organic&utm_content=ReasonsToBecomeCES
Quatman, C. E., Quatman-Yates, C. C., & Hewett, T. E. (2010). A ‘plane’ explanation of anterior cruciate ligament injury mechanisms: a systematic review. Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.), 40(9), 729–746. https://doi.org/10.2165/11534950-000000000-00000
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information on this blog site is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters and issues that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card


