Can understanding the body’s hinge joints and how they operate help with mobility and flexibility problems and manage conditions for individuals with difficulty fully bending or extending their fingers, toes, elbows, ankles, or knees?
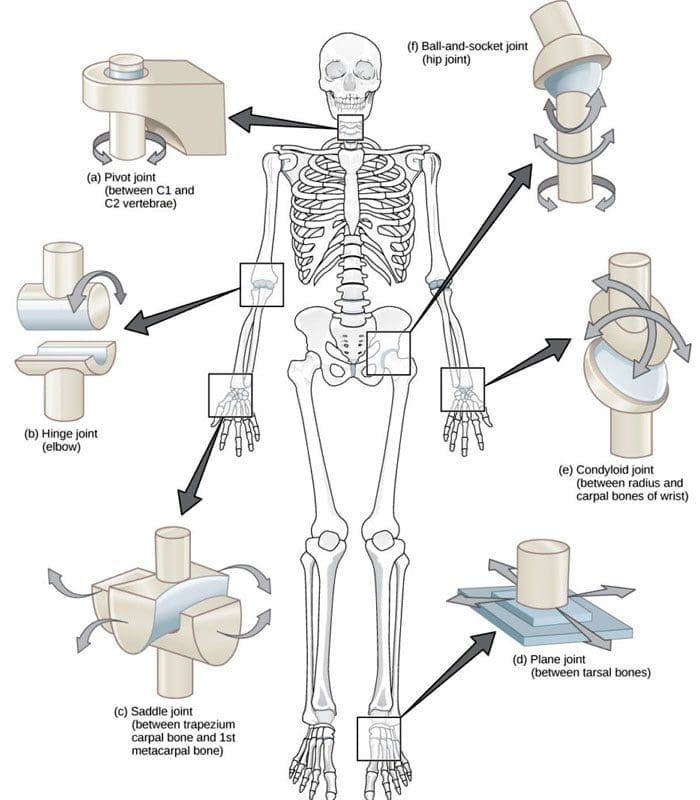
Table of Contents
Hinge Joints
A joint forms where one bone connects to another, allowing motion. Different types of joints differ in structure and movement depending on their location. These include hinge, ball and socket, planar, pivot, saddle, and ellipsoid joints. (Boundless. General Biology, N.D.) Hinge joints are synovial joints that move through one plane of motion: flexion and extension. Hinge joints are found in the fingers, elbows, knees, ankles, and toes and control movement for various functions. Injuries, osteoarthritis, and autoimmune conditions can affect hinge joints. Rest, medication, ice, and physical therapy can help alleviate pain, improve strength and range of motion, and help manage conditions.
Anatomy
A joint is formed by the joining of two or more bones. The human body has three main classifications of joints, categorized by the degree to which they can move. These include: (Boundless. General Biology, N.D.)
Synarthroses
- These are fixed, immovable joints.
- Formed by two or more bones.
Amphiarthroses
- Also known as cartilaginous joints.
- A fibrocartilage disc separates the bones that form the joints.
- These movable joints allow for a slight degree of movement.
Diarthroses
- Also known as synovial joints.
- These are the most common freely mobile joints that allow movement in multiple directions.
- The bones that form the joints are lined with articular cartilage and enclosed in a joint capsule filled with synovial fluid that allows for smooth motion.
Synovial joints are classified into different types depending on differences in structure and the number of motion planes they allow. A hinge joint is a synovial joint that allows movement in one plane of motion, similar to a door hinge that moves forward and backward. Within the joint, the end of one bone is typically convex/pointed outward, with the other concave/rounded inward to allow the ends to fit smoothly. Because hinge joints only move through one plane of movement, they tend to be more stable than other synovial joints. (Boundless. General Biology, N.D.) Hinge joints include:
- The finger and toe joints – allow the fingers and toes to bend and extend.
- The elbow joint – allows the elbow to bend and extend.
- The knee joint – allows the knee to bend and extend.
- The talocrural joint of the ankle – allows the ankle to move up/dorsiflexion and down/plantarflexion.
Hinge joints allow the limbs, fingers, and toes to extend away and bend toward the body. This movement is essential for activities of daily living, such as showering, getting dressed, eating, walking, standing up, and sitting down.
Conditions
Osteoarthritis and inflammatory forms of arthritis can affect any joint (Arthritis Foundation. N.D.) Autoimmune inflammatory forms of arthritis, including rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis, can cause the body to attack its own joints. These commonly affect the knees and fingers, resulting in swelling, stiffness, and pain. (Kamata, M., Tada, Y. 2020) Gout is an inflammatory form of arthritis that develops from elevated levels of uric acid in the blood and most commonly affects the hinge joint of the big toe. Other conditions that affect hinge joints include:
- Injuries to the cartilage within the joints or ligaments that stabilize the outside of the joints.
- Ligament sprains or tears can result from jammed fingers or toes, rolled ankles, twisting injuries, and direct impact on the knee.
- These injuries can also affect the meniscus, the tough cartilage within the knee joint that helps cushion and absorb shock.
Rehabilitation
Conditions that affect hinge joints often cause inflammation and swelling, resulting in pain and limited mobility.
- After an injury or during an inflammatory condition flare-up, limiting active movement and resting the affected joint can reduce increased stress and pain.
- Applying ice can decrease inflammation and swelling.
- Pain-relieving medications like NSAIDs can also help reduce pain. (Arthritis Foundation. N.D.)
- Once the pain and swelling start to subside, physical and/or occupational therapy can help rehabilitate the affected areas.
- A therapist will provide stretches and exercises to help improve the joint range of motion and strengthen the supporting muscles.
- For individuals experiencing hinge joint pain from an autoimmune condition, biologic medications to decrease the body’s autoimmune activity are administered through infusions delivered every several weeks or months. (Kamata, M., Tada, Y. 2020)
- Cortisone injections may also be used to decrease inflammation.
At Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic, we passionately focus on treating patients’ injuries and chronic pain syndromes and improving ability through flexibility, mobility, and agility programs tailored to the individual. Our providers use an integrated approach to create personalized care plans that include Functional Medicine, Acupuncture, Electro-Acupuncture, and Sports Medicine protocols. Our goal is to relieve pain naturally by restoring health and function to the body. If the individual needs other treatment, they will be referred to a clinic or physician best suited for them. Dr. Jimenez has teamed up with the top surgeons, clinical specialists, medical researchers, and premier rehabilitation providers to provide the most effective clinical treatments.
Chiropractic Solutions
References
Boundless. General Biology. (N.D.). 38.12: Joints and Skeletal Movement – Types of Synovial Joints. In. LibreTexts Biology. bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Introductory_and_General_Biology/Book%3A_General_Biology_%28Boundless%29/38%3A_The_Musculoskeletal_System/38.12%3A_Joints_and_Skeletal_Movement_-_Types_of_Synovial_Joints
Arthritis Foundation. (N.D.). Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Foundation. www.arthritis.org/diseases/osteoarthritis
Kamata, M., & Tada, Y. (2020). Efficacy and Safety of Biologics for Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis and Their Impact on Comorbidities: A Literature Review. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(5), 1690. doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051690
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information on this blog site is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card


