With the last article, we talk about how our gut system actually works. With the many microbes that inhabit our intestines, we do try to our best to lead a healthier lifestyle. Here at Injury Medical, local chiropractors and health coaches inform our patients about functional medicine as well as helping them to prevent a leaky gut. Here we will talk more about what the microbiomes in our intestines do when we are exposed to harsh environments.
Table of Contents
The Microbiome
The significant role of the microbiome in the epithelial barrier integrity and breakdown. However, we can’t have a conversation with patients about intestinal permeability and food sensitivities without telling them about the role the microbiome plays.
The Wheat zoomer is rich with data but adds the Gut zoomer with the patients; the results are more accurate.
Microbial Influence on our Intestines
- Immune influence: One of the leading roles that microbiomes play in the immune system is that it generates byproducts of carbohydrates/fiber fermentation that will influence T-cell differentiation. Without the distinction, we will see an increase of being at high risk of autoimmune diseases, allergies, autism, and asthma.
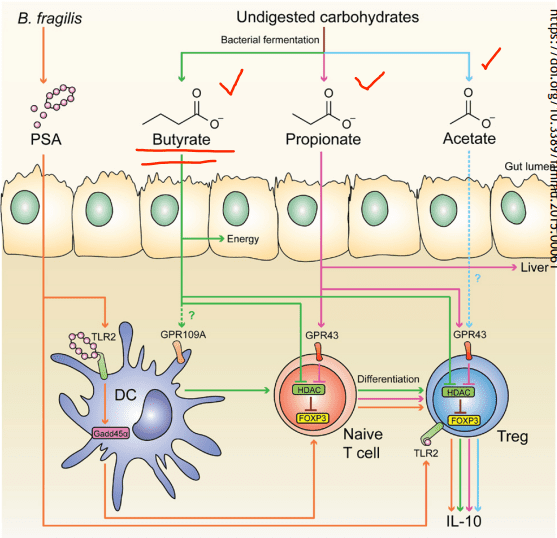
- SCFAs (Short Chain Fatty Acids): The food we consume gets fermented for good bacteria to feed on. SCFAs creates fermented fibers by commensal microbes into Butyrate, Propionate, Acetate. These three are essential to the intestinal immune system. These SCFAs can influence T-cells differentiation differently, but it still gets the same results.
- T-cell Differentiation: naïve T-cells that activate the immune response to T-regs (police cells) to signal B-cells, and it can be a good thing. But if the T-cells activate and differentiate the wrong cells, it will cause inflammation.
When T-cells differentiation is less abundant, there will be a higher incidence of food sensitivities, autoimmune disease, asthma, and allergies. But when there is an abundance of butyrate, the patients have lower rates of colon cancer and colitis.
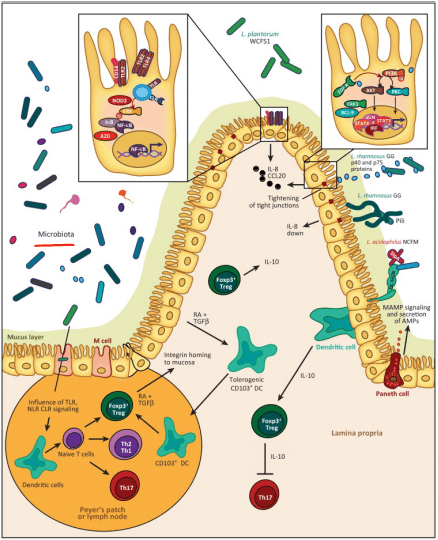
- Tight Junction: Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus rhamnosus are the reinforcers for the tight junction while inducing TLR (toll-like receptors) outside the intestinal epithelial walls, as well as increasing the abundance of zonulin-occludin into the tight junction.
SCFAs also play a vital role in the tight junction by lessening the extent propionate, inducing LOX (lipoxygenase) activity and increasing tight junction’s stability while reducing permeability.
Pathogens/Pathobionts: Can be an influence in the epithelial barriers as they can be opportunistic or conditionally pathogenic. Various pathogens like enteropathogenic E.coli can alternate the tight junction’s system. However, if there is a low abundance of L. plantarum, then it will lead to infections and disruption as well as disorganization of the actin cytoskeletons. This can be reversed by incubating the epithelial cells with L. plantarum to create a high density of actin filaments to the tight junction and repair itself.
- Zonulin, actin, and LPS: In the previous article, zonulin is the ‘gatekeeper’ proteins that are responsible for opening and closing the tight junction. We talked about how if there is a low count of zonulin, it can cause inflammation, but if the zonulins are high, they can increase the IP and may facilitate enteric translocation by disassembling the tight junction. With less zonulin, it can be an overgrowth of b bacteria cells, thus causing more inflammation.
Actins are the structural and functional cells in the tight junction. However, if bacteria enter the actin cell walls, the bacteria will release toxins to the cell walls, it not only damages it but causes it to leak as well. This will make the damage actin cells not only paracellular but also intracellular to the damage actin cell walls.
Actin walls can also be affected when surfactants are involved. Surfactants are food agents and are known to affect the absorption of food substances in the gastrointestinal tract. They are not problematic, but when there is a low count on TEER, it can increase permeability and disband the tight junction.
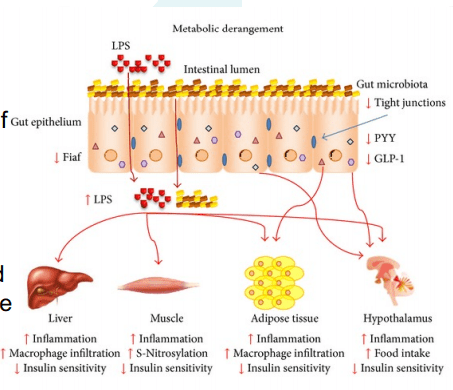
LPS (Lipopolysaccharide) acts as a barrier and is recognized by the immune system as a marker for detecting bacterial pathogen invasion. It’s responsible for the development of inflammatory response in our gut.
Diet and lifestyle
Diet and lifestyle contributions to the epithelial barrier integrity and breakdown. With the Wheat and Gut Zoomer helping out our intestinal barriers. Specific diets and lifestyles can also play effect to what is causing discomfort to our gut. These factors can cause our gut to be an imbalance, gastro discomfort, inflammation on our intestinal epithelial barriers.
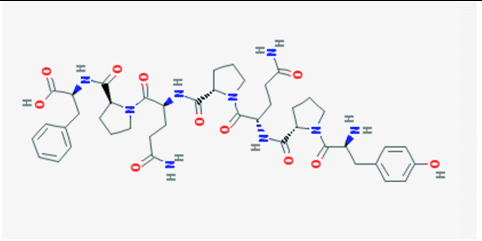
- Gluten: Gliadin is the main peptide that can cause gluten sensitivity. The gliadin protein can bind with many microbes, causing discomfort to our intestines and gut. Plus giving us an autoimmune disease, skin allergens, and chronic illnesses.

- Keto/High Fat Intake: Increase fat meals cause an increase of permeability, and if a patient has a high gram-negative, it will cause problems. But it can be beneficial, to those who don’t have the gram-negative bacteria in their system but, certain microbes like SCFAs do cling onto these fatty substances. In order to give patients an accurate result use both the Gut Zoomer and Wheat Zoomer to better the chances. Higher fat meals suppress beneficial bacteria. Causing a double risk of toxins in the bloodstream as well as inflammation.

- Alcohol: Patients are more willing to give up alcohol than gluten. Alcohol can be a stress reliever but can lead to addiction. It can be one of the causes of redistribution of the junctional proteins. One glass of wine a day is ok, but some patients don’t see alcohol as a mediator for reducing problems.

- Lectins: Lectins are contributors to permeability and impair the integrity of the intestinal epithelial layer, allowing passage through. Antibiotics for WGA can help lower the permeability of the intestinal wall barriers.

- Stress: Stress can cause discomfort and permeability in the intestinal epithelial barrier from high levels of cortisol.
Conclusion
Yes, gluten can cause inflammation in the intestinal epithelial barriers, but many factors that we discussed are also factors that can cause physiological assaults on the barrier’s integrity and stability of the intestinal ecosystem. Dr. Alexander Jimenez informs our patients about the importance of how functional medicine works with the combination of the Gut Zoomer and the Wheat Zoomer. This is not only protecting our gut but by giving us the information on what we can do to prevent a leaky gut.
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information on this blog site is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters and issues that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card