Hamstring injuries are several of the most common types of injuries among athletes. These makeup for the most days or even weeks missed each year amongst AFL football players. The majority of partial or complete tears include either the hamstring muscle belly or the distal musculotendinous junction. However, a proximal hamstring injury is ultimately uncommon. In the total hamstring injury spectrum, it makes up for under 10 percent of hamstring injuries, among other health issues.
Table of Contents
Anatomy
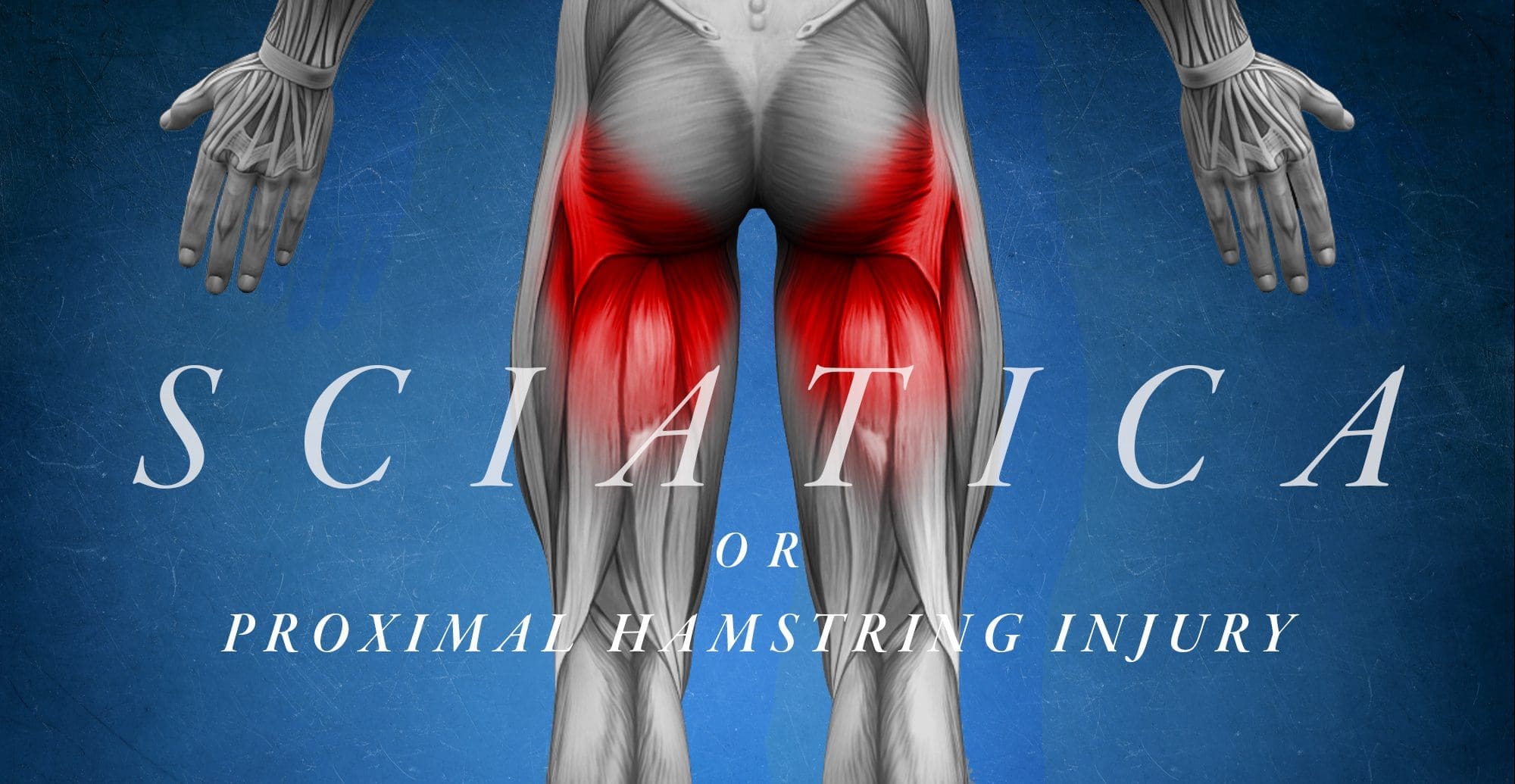
The hamstring makes up the majority of the muscle mass of the rear of the thigh. It is fundamental for shoving off, landing and leaping, especially for volatile activity, such as Pilates. The hamstring consists of 3 muscles, each utilizing a common proximal attachment through a big tendon to the ischial tuberosity of the pelvis or the big bone found in the buttocks. This proximal attachment gives a fixed point from which muscle contraction can impact a more distal activity. The hamstring gives some extension of the hip but the primary activity is movement around the knee. It is largely responsible for knee flexion.
The 3 muscles, the biceps femoris, the semitendinosus, and the semimembranosus, originate in the posterior thigh and attach distally around the knee through tendons to bony landmarks, crossing the joint. The biceps femoris then attaches laterally into the head of the fibula on the exterior of the knee. The semitendinosus and the semimembranosus attach to the medial side of the upper tibia. Because the sciatic nerve travels closely along with the attachment of the proximal hamstring tendon to the ischium, it may become injured along with the hamstring and ultimately cause the well-known symptoms of sciatica.
Mechanism of Injury
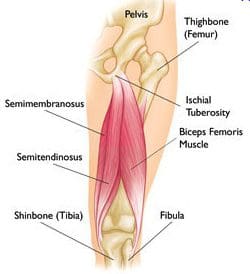
The proximal hamstring tendon can become injured through progressive stretching or through sudden and intense contraction when the hip is forcefully flexed over an extended knee. In younger patients with an average proximal hamstring tendon, this can occur through sprinting or hurdling, however, the most common athletes affected in this instance involves waterskiiers who fall forward with an extended knee. In elderly patients, proximal hamstring injuries occur through a different type of trauma, such as slipping on a wet surface or even doing the “splits” inadvertently.
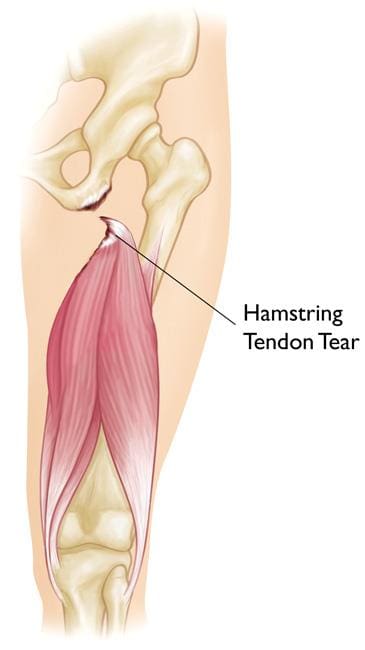
Proximal hamstring injuries could include complete tendon ruptures or incomplete/partial tears. In young patients, the bone together with the tendon is frequently avulsed or fractured in the pelvis or the ischium. In older patients, the tendon usually avulses or tears from the bone of the ischium at its attachment point. Occasionally, the tendon may tear in its midsubstance, leaving a stump of tendon still attached to the bone. Frequently this type of injury is referred to as a partial tear.
Diagnosis for Proximal Hamstring Injury
A proximal hamstring injury may commonly occur due to a sports-related injury and/or accident where the patient will experience something “go” deep in their buttocks. If the incident is being observed, the sufferer may often be seen holding their buttock or upper thigh. The person is generally not able to continue with the activity and when on the ground, they may need help to get up and to walk. There is normally immediate pain and weight bearing on the affected leg while it may also be painful to sit on the affected buttock. During the next 24 to 48 hours, there is swelling and bruising which appears over the buttocks region and extends down the rear of the thigh into the lower leg. Occasionally, the patient may also experience a “pins and needles” sensation in the lower leg and/or foot, similar to sciatica. Decreased movement in the foot may be seen with a foot fall. These injuries generally require immediate medical attention to diagnose the health issue.
X-rays are fundamental in younger patients to rule out an avulsion fracture of the ischial tuberosity. Ultrasound may be undertaken and will help determine the presence of a hematoma, or blood collection, in the buttock and upper thigh which can also detect tendon tears. MRI scans are the best choice of diagnosis and it is highly accurate at determining the site of injury, whether the tear is partial or complete and whether there has been any retraction of the tendon end to the thigh.
Treatment for Proximal Hamstring Injury
Initial treatment for proximal hamstring injury must be symptomatic, where measures will be taken to help decrease pain and swelling with icing, analgesia, and the utilization of crutches to help walking. As the pain begins to settle, a few gentle movements of the leg may be undertaken along with the aid of a healthcare professional. When the diagnosis of a proximal hamstring injury is made, it’s fundamental to follow-up with the proper treatment choices.
Conservative treatment using a rehabilitation program may be appropriate in sedentary older patients or in those with partial tendon tears at which a significant percentage of this tendon is still intact. Conservative treatment is usually also undertaken in most instances of bone avulsion fracture where the bone fragment is sitting near the ischium. Surgery is generally recommended for younger, athletic patients or for elderly victims where there is a complete tendon tear.
Surgery generally involves an overnight stay in the hospital and the process itself is performed under general anesthesia. An incision is made in the buttock/upper thigh where the torn tendon end is identified, mobilized if it’s retracted down to the thigh and repaired back down onto the bone utilizing bone anchors or transosseous sutures. The sciatic nerve is also protected during the surgery. After surgery, painkillers may be required. Healthcare professionals may recommend patients to rest lying on their back with a pillow under the knees to allow the hamstring to be in a relaxed position.
Differential Diagnosis of Hip Pain and Discomfort
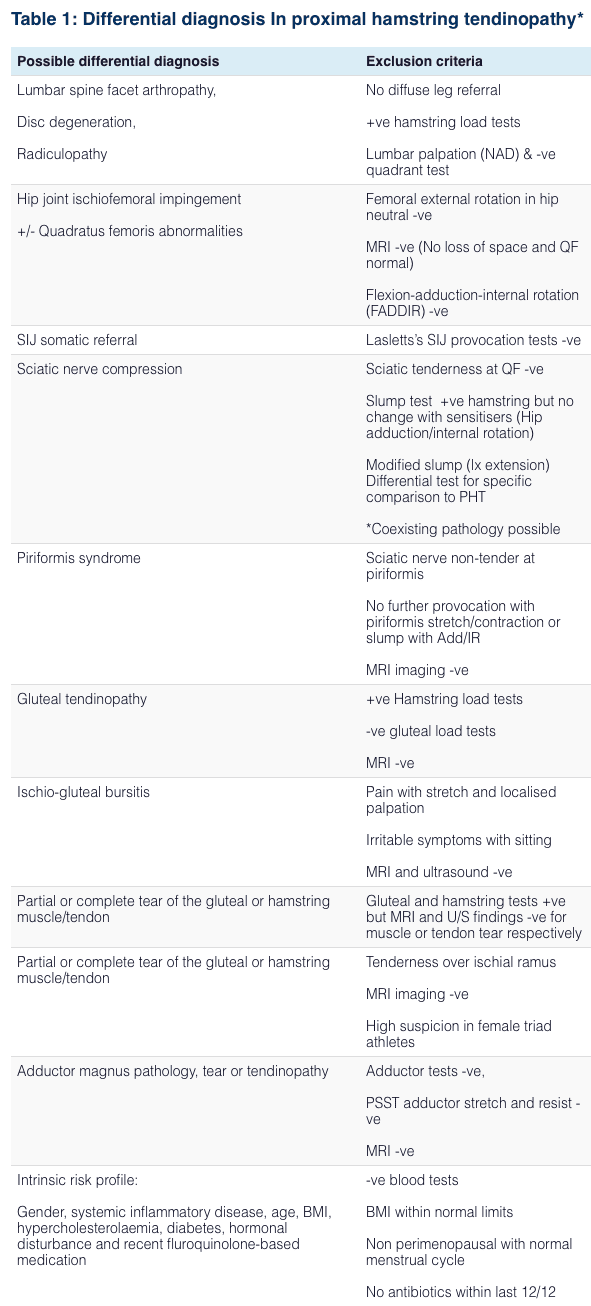

Tendon injuries are common health issues which frequently affect the athletic population. While Achilles tendon and patella tendon injuries are some of the most well-known types of tendon injuries, proximal hamstring injuries can still affect many athletes. Proximal hamstring injuries are health issues which can cause a variety or problems for people if they’re not properly diagnosed and treated. Understanding the differences between proximal hamstring injuries and it’s symptoms, including sciatica, can help both the patient and the doctor achive recovery. – Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T. Insight
Fibromyalgia Magazine
The purpose of the article was to discuss proximal hamstring injuries and sciatica. It has also been observed that patients with proximal hamstring injuries may confuse their symptoms for sciatica. The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal and nervous health issues as well as functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. To further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900 .
Curated by Dr. Alex Jimenez
Additional Topic Discussion: Severe Sciatica
Back pain is one of the most prevalent causes of disability and missed days at work worldwide. Back pain attributes to the second most common reason for doctor office visits, outnumbered only by upper-respiratory infections. Approximately 80 percent of the population will experience back pain at least once throughout their life. Your spine is a complex structure made up of bones, joints, ligaments, and muscles, among other soft tissues. Injuries and/or aggravated conditions, such as herniated discs, can eventually lead to symptoms of sciatica, or sciatic nerve pain. Sports injuries or automobile accident injuries are often the most frequent cause of painful symptoms, however, sometimes the simplest of movements can have these results. Fortunately, alternative treatment options, such as chiropractic care, can help ease sciatic nerve pain, or sciatica, through the utilization of spinal adjustments and manual manipulations, ultimately improving pain relief.
Formulas for Methylation Support
XYMOGEN’s Exclusive Professional Formulas are available through select licensed health care professionals. The internet sale and discounting of XYMOGEN formulas are strictly prohibited.
Proudly, Dr. Alexander Jimenez makes XYMOGEN formulas available only to patients under our care.
Please call our office in order for us to assign a doctor consultation for immediate access.
If you are a patient of Injury Medical & Chiropractic Clinic, you may inquire about XYMOGEN by calling 915-850-0900.
For your convenience and review of the XYMOGEN products please review the following link.*XYMOGEN-Catalog-Download
* All of the above XYMOGEN policies remain strictly in force.
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information on this blog site is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters and issues that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card