Can individuals dealing with musculoskeletal trigger points seek non-surgical treatments to reduce pain in their extremities?
Table of Contents
Introduction
The musculoskeletal system has various muscles, tendons, ligaments, and soft tissues that allow the lower and upper extremities to function in multiple tasks that the person is doing. From physical activities to relaxing or just doing errands, the musculoskeletal system has a wonderful relationship with all the various body systems. It helps protect the vital organs from environmental factors and injuries. However, when environmental factors or injuries affect the body, many overlapping risk profiles affect the upper and lower quadrants, thus affecting the muscles and the soft tissues. When the musculoskeletal system starts to feel symptoms of pain and discomfort, it can cause visceral-somatic referred pain in different body locations and cause the development of trigger points in the muscle tissues. This causes the individual to be in excruciating pain and discomfort and is seeking treatment to reduce the pain-like symptoms. Today’s article gives us an understanding of musculoskeletal trigger points and how various non-surgical treatments can alleviate musculoskeletal trigger points in the body. We discuss with certified associated medical providers who consolidate our patients’ information to assess pain-like issues affecting their musculoskeletal system that are correlating to trigger point pain. We also inform and guide patients on various non-surgical treatments and ask their associated medical providers intricate questions to integrate a customized treatment plan to reduce musculoskeletal trigger point pain. Dr. Jimenez, D.C., includes this information as an academic service. Disclaimer.
Understanding Musculoskeletal Trigger Points
Do you often experience pain in your legs, arms, hands, and feet throughout the day? How often do you experience symptoms of stiffness and discomfort in your neck, shoulder, or back? Or do you feel tingling and numbing sensations in your hands and feet? More often than not, many people who are experiencing these overlapping pain issues in their musculoskeletal system might have trigger points in their muscle fibers. Trigger points are part of a painful musculoskeletal condition known as myofascial pain syndrome. This painful musculoskeletal condition constitutes a hyperirritable spot within the taut band of the musculoskeletal system, causing pain when being compressed. (Lavelle et al., 2007) When a person is dealing with musculoskeletal trigger points, they will often experience referred pain and discomfort, motor dysfunction, and autonomic issues. This is because when many individuals experience pain in the upper or lower muscle quadrants, they deal with referred pain from the affected muscles. When the affected muscles have abnormal tender muscle regions, it can lead to impaired movements associated with the affected muscles in any joint area. (Macdonald, 1980)
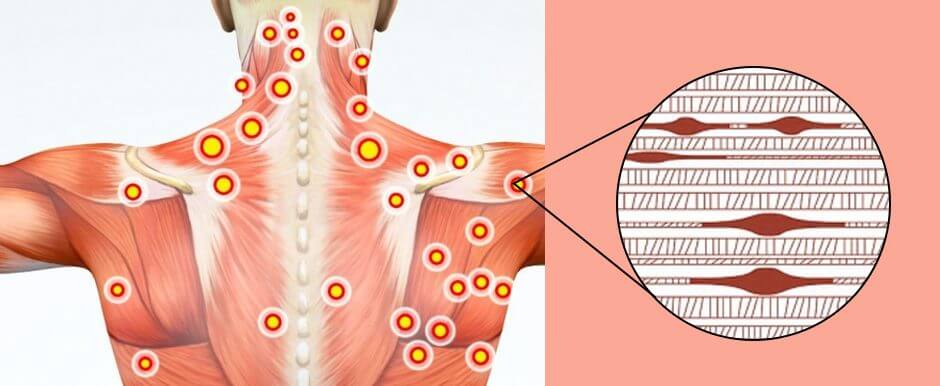
Additionally, musculoskeletal trigger points can be identified as latent or active based on the development of where the pain originates from within the musculoskeletal system. To that point, when environmental factors or injuries develop trigger points, pain-like symptoms like muscle stiffness, dysfunction, and restricted range of motion show up when a pain specialist is assessing a person. (Shah et al., 2015) Fortunately, musculoskeletal trigger points are not difficult to treat once the pain source is located in the musculoskeletal system. This is because non-surgical treatments help manage the pain-like symptoms by inactivating the trigger points and restoring the affected resistant muscles to their full range of motion. (Rubin, 1981)
The Non-Surgical Approach To Wellness-Video
Non-Surgical Treatments For Musculoskeletal Trigger Points
When it comes to treating musculoskeletal trigger points, many individuals seek out various treatments to reduce pain-like symptoms. Since musculoskeletal trigger points can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, it can affect a person’s daily activities and cause them to be miserable. Luckily, musculoskeletal trigger points can be reduced through non-surgical treatments. Non-surgical treatments can vary depending on the pain severity of the trigger points in the musculoskeletal system. At the same time, many individuals can have numerous non-surgical therapies as they are customizable, cost-effective, and personalized for the person’s treatment. Below are some non-surgical treatments that can help alleviate musculoskeletal trigger points.
Chiropractic Care
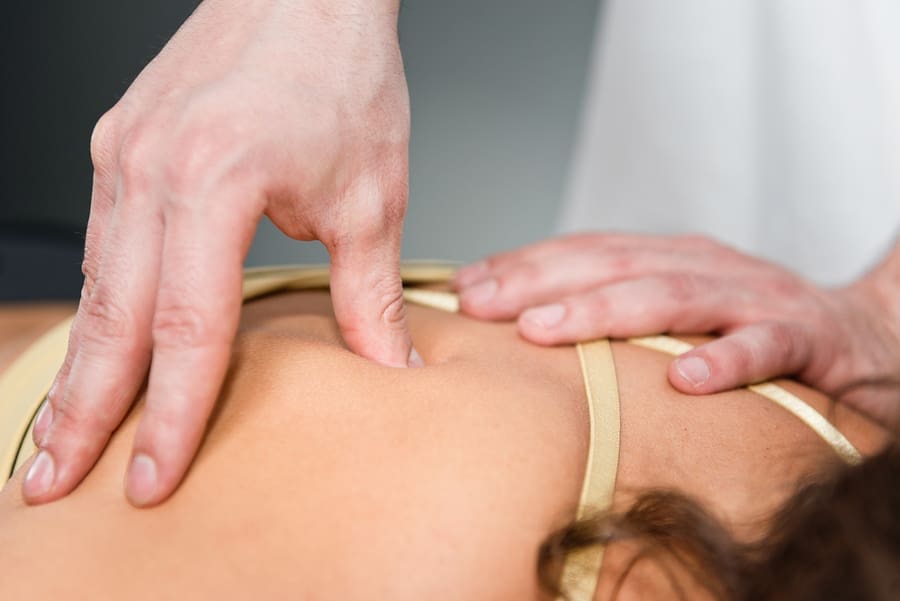
Chiropractic care utilizes mechanical and manual manipulation of the musculoskeletal system and can help reduce the overlapping effects of musculoskeletal trigger points. Chiropractors incorporate various techniques and ischemic pressure to relieve the pain and provide relief. (Vernon & Schneider, 2009) Additionally, chiropractors can locate the trigger points by pressing on the muscle tissue or manipulating the muscle fibers. Chiropractors can also combine massage therapy to relieve trigger points and associated pain symptoms to restore the body to optimal function. This combination can incorporate various techniques to increase blood circulation to the affected muscle, help break down the inflexible scar tissue, and help restore muscle function to the extremities.
Acupuncture
Another form of non-surgical treatment to reduce musculoskeletal trigger points is acupuncture. Acupuncture incorporates solid, thin needles placed on various acupoints in the body by a professional. What acupuncture does is that when the needles are placed in the acupoints of the affected muscle, it can help stimulate the nervous system and help facilitate the body’s natural pain-relieving chemicals to kick-start the healing process. Additionally, when people incorporate acupuncture to reduce musculoskeletal trigger points, the sensory input that is causing them pain is reduced and can provide prolonged relief. (Melzack, 1981)
Lifestyle Adjustments
When it comes to reducing trigger points and combining non-surgical treatments, many individuals dealing with overlapping pain profiles from musculoskeletal trigger points can make lifestyle adjustments to prevent its development. Making small adjustments to a person’s work and living environments can reduce stress from being a co-factor to developing trigger points in the muscle fibers. Other small adjustments like improving posture and employing relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce muscle stress and strain from everyday life. Incorporating non-surgical treatments to reduce and manage musculoskeletal triggers can provide a positive, beneficial result to improve muscle function and allow individuals to live healthier lives.
References
Lavelle, E. D., Lavelle, W., & Smith, H. S. (2007). Myofascial trigger points. Anesthesiol Clin, 25(4), 841-851, vii-iii. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anclin.2007.07.003
Macdonald, A. J. R. (1980). Abnormally tender muscle regions and associated painful movements. Pain, 8(2), 197-205. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3959(88)90007-3
Melzack, R. (1981). Myofascial trigger points: relation to acupuncture and mechanisms of pain. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 62(3), 114-117. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6972204
Rubin, D. (1981). Myofascial trigger point syndromes: an approach to management. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 62(3), 107-110. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6453568
Shah, J. P., Thaker, N., Heimur, J., Aredo, J. V., Sikdar, S., & Gerber, L. (2015). Myofascial Trigger Points Then and Now: A Historical and Scientific Perspective. PM R, 7(7), 746-761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmrj.2015.01.024
Vernon, H., & Schneider, M. (2009). Chiropractic management of myofascial trigger points and myofascial pain syndrome: a systematic review of the literature. J Manipulative Physiol Ther, 32(1), 14-24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmpt.2008.06.012
Disclaimer
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information on this blog site is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters and issues that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card