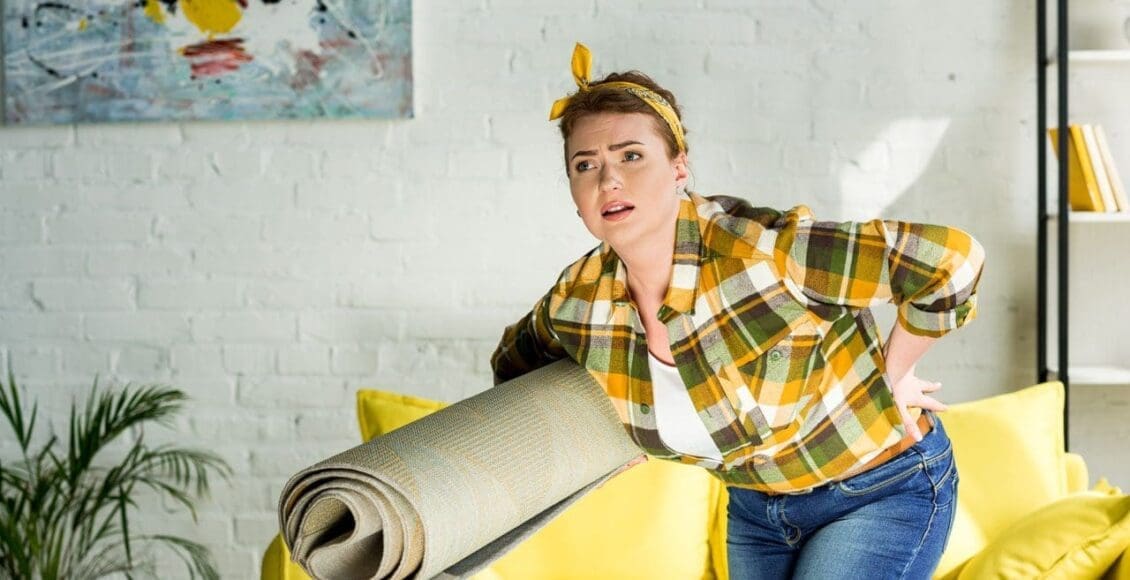
Back discomfort sensations and symptoms could indicate pulled-back muscles. Unless you’ve experienced the condition before, determining the cause can be difficult. A pulled-back muscle can start as a sudden, sharp sting when bending, reaching, or twisting. Or it can present gradually, worsening over a few days. It is a common injury, but if left untreated could take several weeks, and in severe cases, a few months, to heal correctly. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic can help diagnose the problem and develop a customized treatment plan to restore optimal function and health.
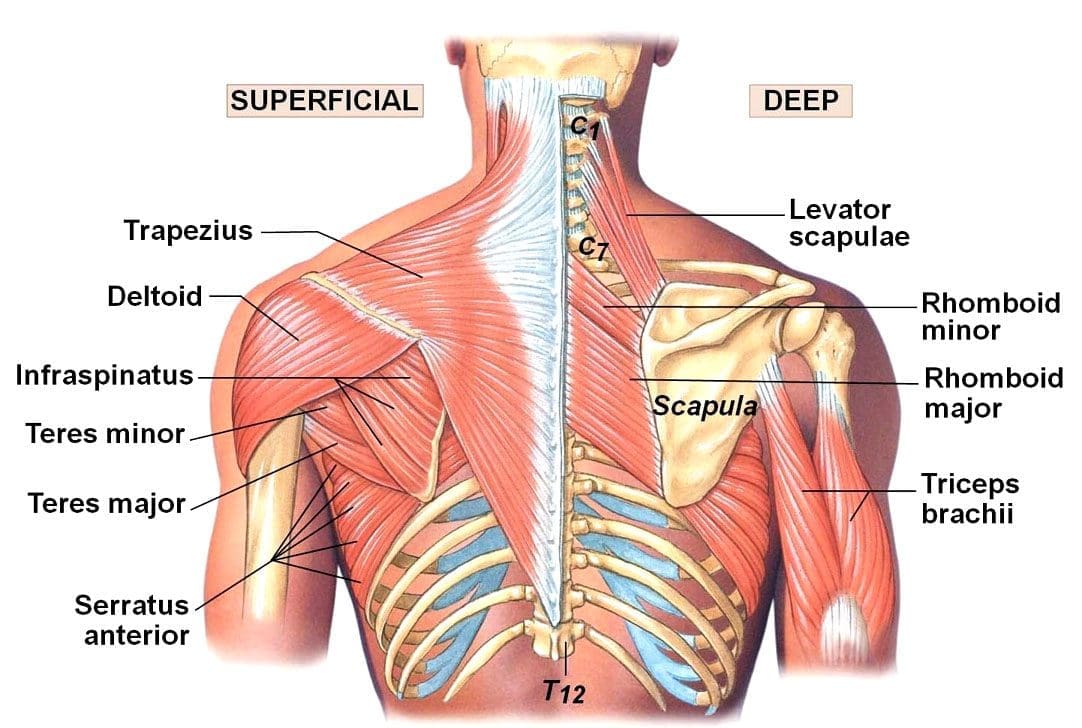
Table of Contents
Pulled Back Muscles
A pulled muscle describes a strained muscle.
- A strain is a muscle or tendon injury that happens when the tissue overstretches or tears.
- When a ligament stretches or tears, it’s called a sprain.
- Most cases can be managed and treated at home.
- But if the symptoms are not improving or make it difficult to move, see a doctor or chiropractor.
Symptoms
Common signs and symptoms of a pulled-back muscle include:
- Swelling
- Tenderness
- Soreness – Sore muscles that feel tight and achy usually indicate a condition that is likely to improve in a few days. More severe soreness could indicate a more significant injury.
- Spasms – A sudden convulsive spasm in the muscle can also indicate a pull. This can feel like a sudden tightening that does not release. The muscle can continue to spasm and lead to other symptoms.
- Cramping – A muscle can cramp can lead to increased tightness whenever trying to use the muscle.
- Pain – Can be characterized as a constant dullness and/or soreness in most situations or, in severe cases, sharp and shooting.
- Discomfort when moving around. If pain flares up when trying to move or use the back muscles is usually an indication that something is wrong.
- Relief during inactivity and rest. When lying down to rest or taking a temporary break, and the symptoms disappear could also be an indication of a pulled-back muscle or another injury.
Causes
The most common causes are:
A Strained Muscle
- This causes some damage to a region of muscle tissue, usually the result of being over-used or torn from another injury.
Sprained Ligaments
- Involves damage to the ligaments in a joint, usually those in the spinal vertebrae.
A Herniated Disc
- This involves damage to the discs that can leak out, irritating the surrounding tissues and nerves and can cause shifting and misalignment of the spine.
These conditions are distinct, but the symptoms can be similar.
Therapies
It is important to consult a medical professional before treating an injury because symptoms of other injuries, such as disc problems or a broken bone, can resemble strains and sprains. Most treatments will utilize:
Ice and Heat
- Ice helps reduce inflammation.
- The faster ice can be applied to a pulled-back muscle, the quicker pain and swelling are reduced, and the healing process can begin.
- Apply a cold pack for 15-20 minutes as soon as the injury occurs.
- Take a 20-minute break between each cold application.
- After the first days, alternate cold therapy with heat to increase circulation.
- Try a 20-20-20 rule: 20 minutes of an ice pack followed by a 20-minute break, then 20 minutes of heat.
- Repeat as necessary, allowing 20 minutes between heat or ice therapy.
Limited Rest
- Right after a muscle strain, limiting physical activity levels and avoiding movements are recommended for a short period.
- After the initial pain subsides, partial activity levels are recommended to help prevent the muscles from weakening.
Compression
- Applying compression bandages or using an active compression system can help reduce swelling and edema and repair damaged tissues faster.
Stretching
- Returning to activities, gentle stretching exercises can improve tissue healing by increasing blood circulation to the injured area.
- Applying heat to the area before stretching can also help.
Strength Training
- Ask a doctor or chiropractor about the right strength exercises for your condition.
- Strength training will develop the muscles to prevent future injuries.
Pain Medication
- Pain levels are an important indicator during the recovery process.
- Pain medications relieve symptoms but do not assist with healing and should only be used short-term to provide relief.
- If you need pain medication, consult your physician to determine the appropriate type and dosage for your situation.
Massage
- Blood circulation to the injured tissues is increased with massage therapy.
Chiropractic
- A chiropractor can diagnose back pain from a muscle or disc injury and develop an individualized treatment plan.
Chiropractic Therapy
References
https://www.aans.org/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Low-Back-Strain-and-Sprain
Allen, Laura. “Case Study: The Use of Massage Therapy to Relieve Chronic Low-Back Pain.” International journal of therapeutic massage & bodywork vol. 9,3 27-30. 9 Sep. 2016, doi:10.3822/ijtmb.v9i3.267
Kumar, Saravana et al. “The effectiveness of massage therapy for the treatment of nonspecific low back pain: a systematic review of systematic reviews.” International journal of general medicine vol. 6 733-41. 4 Sep. 2013, doi:10.2147/IJGM.S50243
https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/injuries-poisoning/sprains-and-other-soft-tissue-injuries/overview-of-sprains-and-other-soft-tissue-injuries
https://www.spine-health.com/conditions/lower-back-pain/exercises-lower-back-muscle-strain
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information on this blog site is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters and issues that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card


