Table of Contents
Introduction
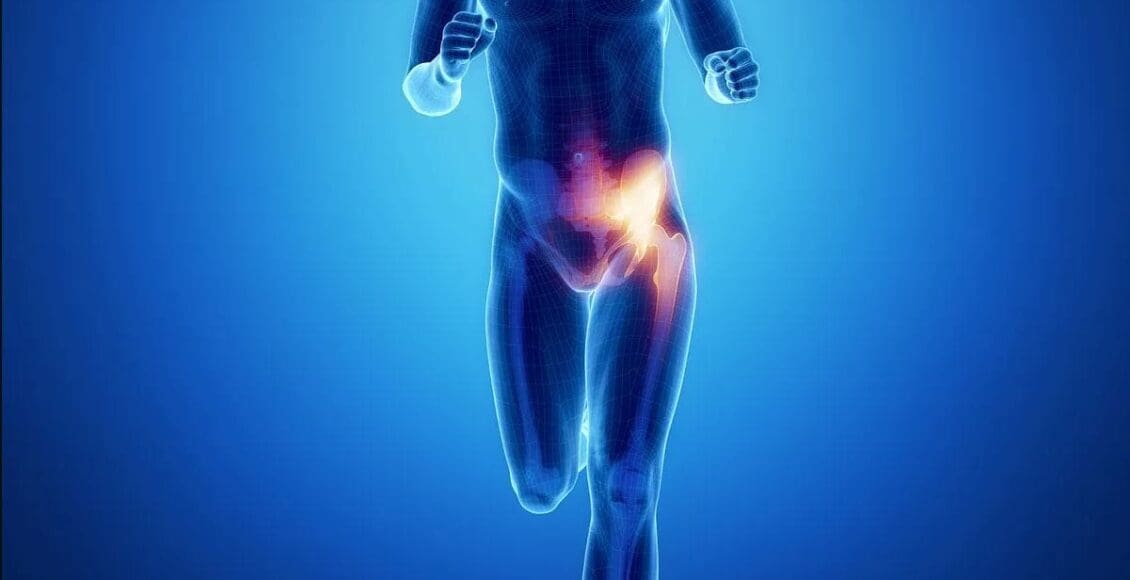
The hips and thighs have a working relationship as their jobs are to maintain stability for the legs and pelvis while supporting the upper body’s weight. These two body groups have various muscles, tendons, and nerves that have specific jobs that allow mobility to the lower body. Many athletes in multiple sports events use their thighs to exert a huge amount of power to be the best. This is due to the adductor muscles in the thighs that allow the athlete to win the event. These adductor muscles are voluminous in size and can become overstretched if the muscles have been worked out too much or injuries have caused dysfunction in the surrounding muscles, causing mobility issues. To that point, the adductor muscles will develop myofascial trigger points and cause hip and thigh pain. Today’s article looks at the two adductor muscles (Longus and Magnus), how myofascial trigger points affect the adductor muscles, and available treatments to manage hip adductor trigger points. We refer patients to certified providers who incorporate multiple methods in the lower body extremities, like thigh and hip pain treatments correlating to myofascial trigger point pain, to aid individuals dealing with pain symptoms along the adductor muscles. We encourage and appreciate patients by referring them to associated medical providers based on their diagnosis, especially when appropriate. We understand that education is an excellent solution to asking our providers complex questions at the patient’s request. Dr. Jimenez, D.C., utilizes this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
Adductor Longus & Adductor Magnus
Have you been dealing with groin pain located near your thighs? Do you feel muscle tenderness or stiffness when stretching your inner thighs? Or have you been feeling unstable in your hips or thighs when walking? Many individuals, especially athletes and older adults, could be experiencing myofascial trigger points associated with groin pain along their adductor muscles. The thighs contain several muscles and functions that allow many people to bend and extend their knees and hips. The adductor muscles allow the legs to move inward toward one another. The adductor muscles have five muscles: magnus, brevi, longus, pectineus, and gracilis. These muscles enable functionality to the thighs and hips, and we will look at two adductor muscles in the inner thighs. The long adductor muscle is a large, fan-shaped muscle that starts from the superior aspect of the pubis bone and travels down to connect at the thigh bone. Studies reveal that the adductor longus is a long and thin muscle with many actions for the thighs, including external/lateral rotation and thigh flexion.
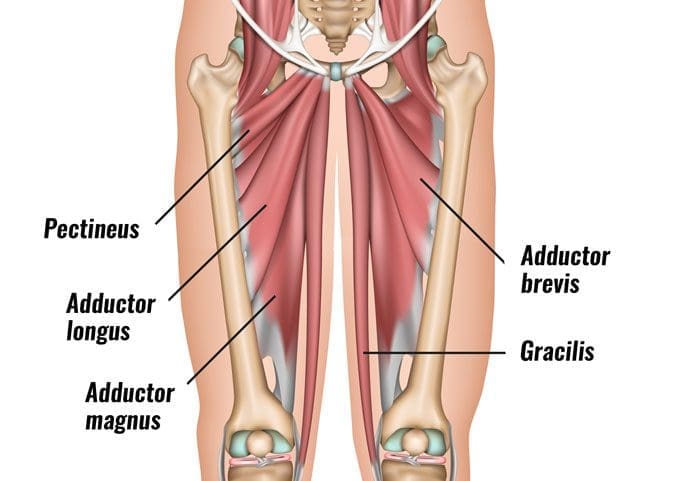
Now the adductor Magnus is a large triangular-shaped muscle of the inner thighs that are important for thigh and hip function and stabilizing the pelvis. Studies reveal that even though the adductor Magnus is a large muscle in the inner thighs, its primary function is to allow the thigh to move in a larger range of motion without any pain inflicted on the thigh muscles. However, the adductor muscle can succumb to various issues affecting the thighs and groin regions of the body that can be overstretched and strain the body.
Myofascial Trigger Points Affecting The Adductor Muscles
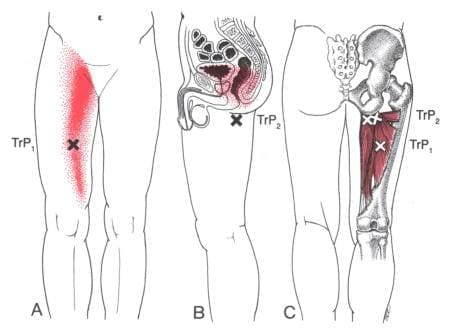
Groin pain is a multi-factorial pain issue that affects the lower limbs, and its often due to muscle strain in the inner thigh muscles. This pain increases during vigorous activities and when there is a sudden twist in the hips. When the adductor muscles suddenly change in motion when the body is active, they can be overstretched and correlate to myofascial trigger points that can affect the inner thigh and groin regions. According to “Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction,” by Dr. Travell, M.D., patients with active myofascial trigger points in the two adductor muscles (Longus and Magnus) would become frequently aware of the pain in their groin and medial thigh. When the adductor muscles have myofascial trigger points in the inner thigh, diagnosing is difficult since the individual thinks they are suffering from groin pain when the pain is in their inner thighs. To that point, studies reveal that many individuals participating in various sports would suffer from groin pain due to myofascial trigger points affecting the adductor muscles. Luckily, there are multiple treatments to reduce the pain in the adductor muscles.
Hip Adductors: Trigger Point Anatomy- Video
Have you been dealing with groin pain when you are walking? What about experiencing unquestionable thigh pain that affects your daily activities? Or does stretching your inner thigh muscles seem difficult, causing muscle tenderness? Many of these symptoms correlate with groin pain associated with myofascial trigger points affecting the adductor muscles in the inner thighs. The adductor muscles allow mobility function to the thighs and enable the hips to have a wide range of motion. When the adductor muscles are overstretched due to a sudden change of hip rotation or injury has occurred on the thighs can lead to referred pain in the groin and inner thighs and develop myofascial trigger points. The video above shows where the trigger points are located in the hip adductor muscles. The video also explains where the pain is localized in the adductor muscles and the symptoms it produces that can affect the lower body extremities. Fortunately, even though diagnosing myofascial trigger points are a bit challenging, available treatments can manage trigger points along the hip adductors.
Available Treatments To Manage Hip Adductor Trigger Points
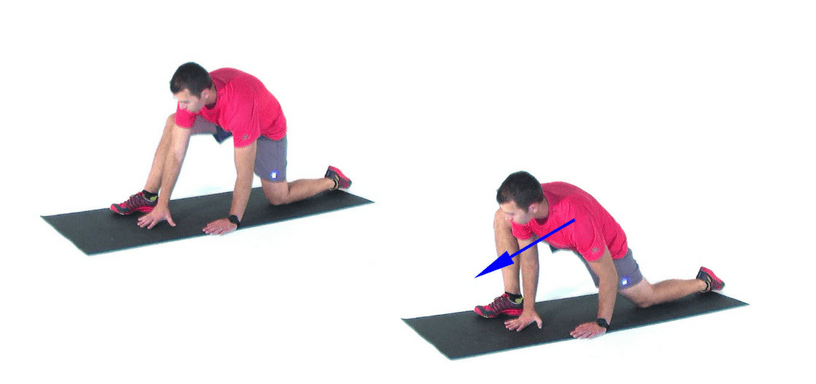
When myofascial trigger points affect the hip adductor muscles, many individuals complain about stiffness in their inner thighs and how they feel miserable when they don’t have mobility from their thighs and hips. As stated earlier, trigger points are a bit challenging when diagnosed, but they are treatable when doctors examine patients dealing with myofascial pain in their hips and thigh muscles. Once the diagnosis is complete, doctors work with pain specialists who can locate the trigger points and devise a treatment plan to relieve the pain. Available treatments like trigger point injections can minimize the pain and reduce the chances of trigger points returning. Other available therapies like exercising or stretching, especially for the hips and thighs. Specific exercises for the hips and thigh muscles can help strengthen the adductor muscles from suffering pain and can help reduce the pain symptoms. Another treatment is applying moist heat on the hip adductor muscles to release the tension from the tight muscles and allow mobility back to the hip adductors.
Conclusion
The adductor muscles work with the hips and thighs to allow a wide range of motions and extension to the knees and hips. The hips and the thighs allow stability to the lower body and support the weight to the upper body. When injuries or sudden changes start to affect the adductor muscles, it can lead to symptoms of groin pain associated with myofascial trigger points. Myofascial trigger points produce tiny nodules in the affected muscle that causes referred pain to the muscle group. When this happens, it causes the body to be dysfunctional and can affect a person’s mobility to function in the world. Luckily myofascial trigger points are treatable through various techniques and treatments that can reduce the chances of trigger points from re-occurring in the body.
References
Jeno, Susan H, and Gary S Schindler. “Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Thigh Adductor Magnus Muscle.” In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL), StatPearls Publishing, 1 Aug. 2022, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534842/.
Sedaghati, Parisa, et al. “Review of Sport-Induced Groin Injuries.” Trauma Monthly, Kowsar, Dec. 2013, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3864393/.
Shahid, Shahab. “Adductor Longus Muscle.” Kenhub, Kenhub, 30 June 2022, https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/adductor-longus-muscle.
Simons, D. G., and L. S. Simons. Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual: Vol. 2:the Lower Extremities. Williams & Wilkins, 1999.
Takizawa, M, et al. “Why Adductor Magnus Muscle Is Large: The Function Based on Muscle Morphology in Cadavers.” Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 27 Apr. 2012, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22537037/.
van de Kimmenade, R J L L, et al. “A Rare Case of Adductor Longus Muscle Rupture.” Case Reports in Orthopedics, Hindawi Publishing Corporation, 2015, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4397006/.
Disclaimer
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information on this blog site is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters and issues that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card