Manual Therapy for Migraine Treatment In El Paso
Manual therapy migraine treatment, or manipulative therapy, is a physical treatment approach which utilizes several specific hands-on techniques to treat a variety of injuries and/or conditions. Manual therapy is commonly used by chiropractors, physical therapists and massage therapists, among other qualified and experienced healthcare professionals, to diagnose and treat soft tissue and joint pain. Many healthcare specialists recommend manual therapy, or manipulative therapy as a treatment for migraine headache pain. The purpose of the following article is to educate patients on the effects of manual therapies for migraine treatment.
Table of Contents
Manual Therapies for Migraine: a Systematic Review
Abstract
Migraine occurs in about 15% of the general population. Migraine is usually managed by medication, but some patients do not tolerate migraine medication due to side effects or prefer to avoid medication for other reasons. Non-pharmacological management is an alternative treatment option. We systematically reviewed randomized clinical trials (RCTs) on manual therapies for migraine. The RCTs suggest that massage therapy, physiotherapy, relaxation and chiropractic spinal manipulative therapy might be equally effective as propranolol and topiramate in the prophylactic management of migraine. However, the evaluated RCTs had many methodological shortcomings. Therefore, any firm conclusion will require future, well-conducted RCTs on manual therapies for migraine.
Keywords: Manual therapies, Massage, Physiotherapy, Chiropractic, Migraine, Treatment
Introduction
Migraine is usually managed by medication, but some patients do not tolerate acute and/or prophylactic medicine due to side effects, or contraindications due to co-morbidity of myocardial disorders or asthma among others. Some patients wish to avoid medication for other reasons. Thus, non-pharmacological management such as massage, physiotherapy and chiropractic may be an alternative treatment option. Massage therapy in Western cultures uses classic massage, trigger points, myofascial release and other passive muscle stretching among other treatment techniques which are applied to abnormal muscle tissue. Modern physiotherapy focuses on rehabilitation and exercise, while manual treatment emphasis postural corrections, soft tissue work, stretching, active and passive mobilization and manipulation techniques. Mobilization is commonly defined as movement of joints within the physiological range of motion [1]. The two most common chiropractic techniques are the diversified and Gonstead, which are used by 91 and 59% of chiropractors [2]. Chiropractic spinal manipulation (SM) is a passive-controlled maneuver which uses a directional high-velocity, low-amplitude thrusts directed at a specific joint past the physiological range of motion, without exceeding the anatomical limit [1]. The application and duration of the different manual treatments varies among those who perform it. Thus, manual treatment is not necessarily as uniform as, for instance, specific treatment with a drug in a certain dose.
This paper systematically review randomized controlled trials (RCTs) assessing the efficacy of manual therapies on migraine, i.e., massage, physiotherapy and chiropractic.
Method
The literature search was done on CINAHL, Cochrane, Medline, Ovid and PubMed. Search words were migraine and chiropractic, manipulative therapy, massage therapy, osteopathic treatment, physiotherapy or spinal mobilization. All RCTs written in English using manual therapy on migraine were evaluated. Migraine was preferentially classified according to the criteria of the International Headache Societies from 1988 or its revision from 2004, although it was not an absolute requirement [3, 4]. The studies had to evaluate at least one migraine outcome measure such as pain intensity, frequency, or duration. The methodological quality of the included RCT studies was assessed independently by the authors. The evaluation covered study population, intervention, measurement of effect, data presentation and analysis (Table 1). The maximum score is 100 points and ?50 points considered to be methodology of good quality [5–7].
Results
The literature search identified seven RCT on migraine that met our inclusion criteria, i.e., two massage therapy studies [8, 9], one physiotherapy study [10] and four chiropractic spinal manipulative therapy studies (CSMT) [11–14], while we found no RCTs studies on spinal mobilization or osteopathic as a intervention for migraine.
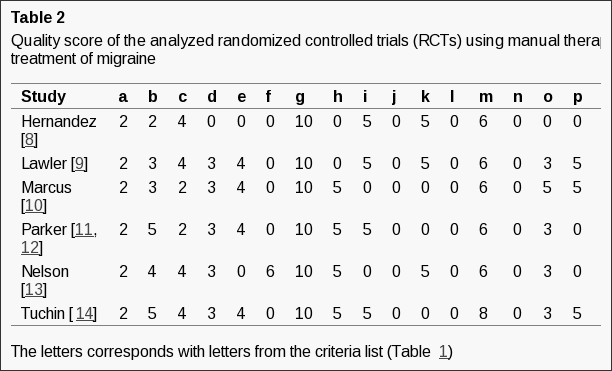
Methodological Quality of the RCTs
Table 2 shows the authors average methodological score of the included RCT studies [8–14]. The average score varied from 39 to 59 points. Four RCTs were considered to have a good quality methodology score (?50), and three RCTs had a low score.
Randomized Controlled Trials
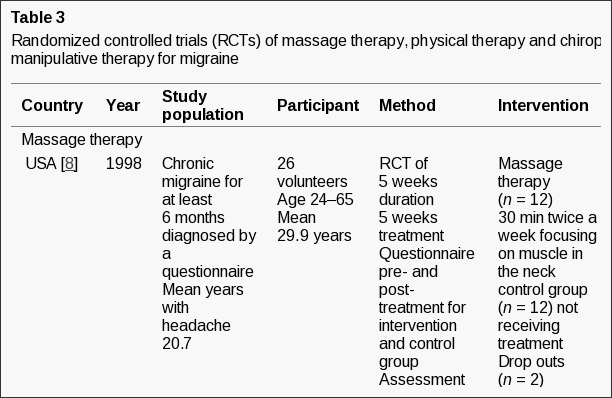
Table 3 shows details and the main results of the different RCT studies [8–14].
Massage Therapy
An American study included 26 participants with chronic migraine diagnosed by questionnaire [8]. Massage therapy had a statistically significant effect on pain intensity as compared with controls. Pain intensity was reduced 71% in the massage group and unchanged in the control group. Interpretation of the data is otherwise difficult and results on migraine frequency and duration are missing.
A New Zealand study included 48 migraineurs diagnosed by questionnaire [9]. The mean duration of a migraine attack was 47 h, and 51% of the participants had more than one attack per month. The study included a 3 week follow-up period. The migraine frequency was significantly reduced in the massage group as compared with the control group, while the intensity of attacks was unchanged. Results on migraine duration are missing. Medication use was unchanged, while sleep quality was significantly improved in the massage group (p < 0.01), but not in the control group.

Physical Therapy
An American physical therapy study included female migraineurs with frequent attacks diagnosed by a neurologist according to the criteria of the International Headache Society [3, 10]. Clinical effect was defined as >50% improvement in headache severity. Clinical effect was observed in 13% of the physical therapy group and 51% of the relaxation group (p < 0.001). The mean reduction in headache severity was 16 and 41% from baseline to post-treatment in the physical therapy and relaxation groups. The effect was maintained at 1 year follow-up in both groups. A second part of the study offered persons without clinical effect in the first part of the study, the other treatment option. Interestingly, clinical effect was observed in 55% of those whom received physical therapy in the second round who had no clinical effect from relaxation, while 47% had clinical effect from relaxation in the second round. The mean reduction in headache severity was 30 and 38% in the physical therapy and relaxation groups. Unfortunately, the study did not include a control group.

Chiropractic Spinal Manipulative Treatment
An Australian study included migraineurs with frequent attacks diagnosed by a neurologist [11]. The participants were divided into three study groups; cervical manipulation by chiropractor, cervical manipulation by physiotherapist or physician, and cervical mobilization by physiotherapist or physician. The mean migraine attack duration was skewed in the three groups, as it was much longer in cervical manipulation by chiropractor (30.5 h) than cervical manipulations by physiotherapist or physician (12.2 h) and cervical mobilization groups (14.9 h). The study had several investigators and the treatment within each group was beside the mandatory requirements free for the therapists. No statistically significant differences were found between the three groups. Improvement was observed in all three groups post-treatment (Table 3). Prior to the trial, chiropractors were confident and enthusiastic about the efficacy of cervical manipulation, while physiotherapists and physicians were doubtful about the relevance. The study did not include a control group although cervical mobilization is mentioned as the control group in the paper. A follow-up 20 months after the trial showed further improvement in the all three groups (Table 3) [12].

An American study included 218 migraineurs diagnosed according to the criteria of the International Headache Society by chiropractors [13]. The study had three treatment groups, but no control group. The headache intensity on days with headaches was unchanged in all three groups. The mean frequency was reduced equally in the three groups (Table 3). Over the counter (OTC) medication was reduced from baseline to 4 weeks post-treatment with 55% in the CSMT group, 28% in the amitriptyline group and 15% in the combined CSMT and amitriptyline group.
The second Australian study was based on questionnaire diagnoses on migraine [14]. The participants had migraine for mean 18.1 years. The effect of CSMT was significant better than the control group (Table 3). The mean reduction of migraine frequency, intensity and duration from baseline to follow-up were 42, 13, and 36% in CSMT group, and 17, 5, and 21% in the control group (data calculated by the reviewers based on figures from the paper).
Discussion
Methodological Considerations
The prevalence of migraine was similar based on a questionnaire and a direct physician conducted interview, but it was due to equal positive and negative misclassification by the questionnaire [15]. A precise headache diagnosis requires an interview by a physicians or other health professional experienced in headache diagnostics. Three of the seven RCTs ascertained participants by a questionnaire, with the diagnostic uncertainty introduced by this (Table 3).
The second American study included participants with at least four headache days per months [13]. The mean headache severity on days with headache at baseline varied from 4.4 to 5.0 on a 0–10 box scale in the three treatment groups. This implies that the participants had co-occurrence of tension-type headache, since tension-type headache intensity usually vary between 1 and 6 (mild or moderate), while migraine intensity can vary between 4 and 9 (moderate or severe), but usually it is a severe pain between 7 and 9 [16, 17]. The headache severity on days with headache was unchanged between baseline and at follow-up, indicating that the effect observed was not exclusively due to an effect on migraine, but also an effect on tension-type headache.
RCTs that include a control group are advantageous to RCTs that compare two active treatments, since the effect in the placebo group rarely is zero and often varies. An example is RCTs on acute treatment of migraine comparing the efficacy of subcutaneous sumatriptan and placebo showed placebo responses between 10 and 37%, while the therapeutic effect, i.e., the efficacy of sumatriptan minus the efficacy of placebo was similar [18, 19]. Another example is a RCT on prophylactic treatment of migraine, comparing topiramate and placebo [20]. The attack reduction increased along with increasing dose of topiramate 50, 100 and 200 mg/day. The mean migraine attack frequency was reduced from 1.4 to 2.5 attacks per month in the topiramate groups and 1.1 attacks per month in the placebo group from baseline, with mean attack frequencies varying from 5.1 to 5.8 attacks per month in the four groups.
Thus, interpretation of the efficacy in the four RCTs without a control group is not straight forward [9–12]. The methodological quality of all seven RCTs had room for improvement as the maximum score 100 was far from expectation, especially a precise migraine diagnosis is important.
Several of the studies relatively include a few participants, which might cause type 2 errors. Thus, power calculation prior to the study is important in the future studies. Furthermore, the clinical guidelines from the International Headache Society should be followed, i.e., frequency is a primary end point, while duration and intensity can be secondary end points [21, 22].

Dr. Alex Jimenez’s Insight
Manual therapies, such as massage therapy, physical therapy and chiropractic spinal manipulative treatment are several well-known migraine treatment approaches recommended by healthcare professionals to help improve as well as manage the painful symptoms associated with the condition. Patients who are unable to use drugs and/or medications, including those who may prefer to avoid using these, can benefit from manual therapies for migraine treatment, according to the following article. Evidence-based research studies have determined that manual therapies might be equally as effective for migraine treatment as drugs and/or medications. However, the systematic review determined that future, well-conducted randomized clinical trials on the use of manual therapies for migraine headache pain are required to conclude the findings.
Results
The two RCTs on massage therapy included relatively a few participants, along with shortcomings mentioned in Table 3 [8, 9]. Both studies showed that massage therapy was significantly better than the control group, by reducing migraine intensity and frequency, respectively. The 27–28% (34–7% and 30–2%) therapeutic gain in migraine frequency reduction by massage therapy is comparable with the 6, 16 and 29% therapeutic gain in migraine frequency reduction by prophylactic treatment with topiramate 50, 100 and 200 mg/day [20].
The single study on physiotherapy is large, but do not include a control group [10]. The study defined responders to have 50% or more reduction in migraine intensity. The responder rate to physical therapy was only 13% in the first part of the study, while it was 55% in the group that did not benefit from relaxation, while the responder rate to relaxation was 51% in the first part of the study and 47% in the group that did not benefit from physical therapy. A reduction in migraine intensity often correlates with reduced migraine frequency. For comparison, the responder rate was 39, 49, 47 and 23% among those who received topiramate 50, 100 and 200 mg/day and placebo as defined by 50% or more reduction in migraine frequency [20]. A meta-analysis of 53 studies on prophylactic treatment with propranolol showed a mean 44% reduction in migraine activity [23]. Thus, it seems that physical therapy and relaxation has equally good effect as topiramate and propranolol.
Only one of the four RCTs on chiropractic spinal manipulative therapy (CSMT) included a control group, while the other studies compared with other active treatment [11–14]. The first Australian study showed that the migraine frequency was reduced in all three groups when baseline was compared with 20 months post trail [11, 12]. The chiropractors were highly motivated to CSMT treatment, while physicians and physiotherapist were more sceptical, which might have influenced on the result. An American study showed that CSMT, amitriptyline and CSMT + amitriptyline reduced the migraine frequency 33, 22 and 22% from baseline to post-treatment (Table 3). The second Australian study found that migraine frequency was reduced 35% in the CSMT group, while it was reduced 17% in the control group. Thus, the therapeutic gain is equivalent to that of topiramate 100 mg/day and the efficacy is equivalent to that of propranolol [20, 23].
Three case reports raise concerns about chiropractic cervical SMT, but a recent systematic review found no robust data concerning the incidence or the prevalence of adverse reactions following chiropractic cervical SMT [24–27]. When to refer migraine patients to manual therapies? Patients not responding or tolerating prophylactic medication or who wish to avoid medication for other reasons, can be referred to massage therapy, physical therapy or chiropractic spinal manipulative therapy, as these treatments are safe with a few adverse reactions [27–29].
Conclusion
Current RCTs suggest that massage therapy, physiotherapy, relaxation and chiropractic spinal manipulative therapy might be equally efficient as propranolol and topiramate in the prophylactic management of migraine. However, a firm conclusion requires, in future, well-conducted RCTs without the many methodological shortcomings of the evaluated RCTs on manual therapies. Such studies should follow clinical trial guidelines from the International Headache Society [21, 22].
Conflict of Interest
None declared.
Open Access: This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits any use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
In conclusion, chiropractors, physical therapists and massage therapists, among other qualified and experienced healthcare professionals, recommend manual therapies as a treatment for migraine headache pain. The purpose of the article was to educate patients on the effects of manual therapies for migraine treatment. Furthermore, the systematic review determined that future, well-conducted randomized clinical trials are required to conclude the findings. Information referenced from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic as well as to spinal injuries and conditions. To discuss the subject matter, please feel free to ask Dr. Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900 .
Curated by Dr. Alex Jimenez
1. Esposito S, Philipson S. Spinal adjustment technique the chiropractic art. Alexandria: Craft Printing; 2005.
2. Cooperstein R, Gleberson BJ. Technique systems in chiropractic. 1. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 2004.
3. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (1988) Classification and diagnostic criteria for headache disorders, cranial neuralgias and facial pain. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. Cephalalgia 8 (suppl 7):1–96 [PubMed]
4. Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Society (2004) The international classification of headache disorders, 2nd edn, Cephalagia 24 (suppl 1):1–160 [PubMed]
5. Ter Riet G, Kleijnen J, Knipschild P. Acupuncture and chronic pain: a criteria-based meta-analysis. J Clin Epidemiol. 1990;43:1191–1199. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(90)90020-P. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
6. Koes BW, Assendelft WJ, Heijden GJ, Bouter LM, Knipschild PG. Spinal manipulation and mobilisation for back and neck pain: a blinded review. BMJ. 1991;303:1298–1303. doi: 10.1136/bmj.303.6813.1298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
7. Fernandez-de-las-Penas C, Alonso-Blanco C, San-Roman J, Miangolarra-Page JC. Methodological quality of randomized controlled trials of spinal manipulation and mobilization in tension-type headache, migraine, and cervicogenic headache. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2006;36:160–169. [PubMed]
8. Hernandez-Rief M, Dieter J, Field T, Swerdlow B, Diego M. Migraine headache reduced by massage therapy. Int J Neurosci. 1998;96:1–11. doi: 10.3109/00207459808986453. [Cross Ref]
9. Lawler SP, Cameron LD. A randomized, controlled trial of massage therapy as a treatment for migraine. Ann Behav Med. 2006;32:50–59. doi: 10.1207/s15324796abm3201_6. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
10. Marcus DA, Scharff L, Mercer S, Turk DC. Nonpharmacological treatment for migraine: incremental utility of physical therapy with relaxation and thermal biofeedback. Cephalalgia. 1998;18:266–272. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-2982.1998.1805266.x. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
11. Parker GB, Tupling H, Pryor DS. A controlled trial of cervical manipulation of migraine. Aust NZJ Med. 1978;8:589–593. [PubMed]
12. Parker GB, Pryor DS, Tupling H. Why does migraine improve during a clinical trial? Further results from a trial of cervical manipulation for migraine. Aust NZJ Med. 1980;10:192–198. [PubMed]
13. Nelson CF, Bronfort G, Evans R, Boline P, Goldsmith C, Anderson AV. The efficacy of spinal manipulation, amitriptyline and the combination of both therapies for the prophylaxis of migraine headache. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 1998;21:511–519. [PubMed]
14. Tuchin PJ, Pollard H, Bonello R. A randomized controlled trial of chiropractic spinal manipulative therapy for migraine. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2000;23:91–95. doi: 10.1016/S0161-4754(00)90073-3. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
15. Rasmussen BK, Jensen R, Olesen J. Questionnaire versus clinical interview in the diagnosis of headache. Headache. 1991;31:290–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1991.hed3105290.x. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
16. Lundquist YC, Benth JS, Grande RB, Aaseth K, Russell MB. A vertical VAS is a valid instrument for monitoring headache pain intensity. Cephalalgia. 2009;29:1034–1041. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01833.x. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
17. Rasmussen BK, Olesen J. Migraine with aura and migraine without aura: an epidemiological study. Cephalalgia. 1992;12:221–228. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-2982.1992.1204221.x. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
18. Ensink FB. Subcutaneous sumatriptan in the acute treatment of migraine. Sumatriptan International Study Group. J Neurol. 1991;238(suppl 1):S66–S69. doi: 10.1007/BF01642910. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
19. Russell MB, Holm-Thomsen OE, Rishoj NM, Cleal A, Pilgrim AJ, Olesen J. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study of subcutaneous sumatriptan in general practice. Cephalalgia. 1994;14:291–296. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-2982.1994.1404291.x. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
20. Brandes JL, Saper JR, Diamond M, Couch JR, Lewis DW, Schmitt J, Neto W, Schwabe S, Jacobs D, MIGR-002 Study Group Topiramate for migraine prevention: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2004;291:965–973. doi: 10.1001/jama.291.8.965. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
21. Tfelt-Hansen P, Block G, Dahlöf C, Diener HC, Ferrari MD, Goadsby PJ, Guidetti V, Jones B, Lipton RB, Massiou H, Meinert C, Sandrini G, Steiner T, Winter PB, International Headache Society Clinical trials Subcommittee Guidelines for controlled trials of drugs in migraine: 2nd ed. Cephalalgia. 2000;20:765–786. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-2982.2000.00117.x. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
22. Silberstein S, Tfelt-Hansen P, Dodick DW, Limmroth V, Lipton RB, Pascual J, Wang SJ, Task Force of the International Headache Society Clinical Trials Subcommittee Guidelines for controlled trials of prophylactic treatment of chronic migraine in adults. Cephalalgia. 2008;28:484–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01555.x. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
23. Holroyd KA, Penzien DB, Cordingley GE. Propranolol in the management of recurrent migraine: a meta-analytic review. Headache. 1991;31:333–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1991.hed3105333.x. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
24. Khan AM, Ahmad N, Li X, Korsten MA, Rosman A. Chiropractic sympathectomy: carotid artery dissection with oculosympathetic palsy after chiropractic manipulation of the neck. Mt Sinai J Med. 2005;72:207–210. [PubMed]
25. Morelli N, Gallerini S, Gori S, Chiti A, Cosottini M, Orlandi G, Murri L. Intracranial hypotension syndrome following chiropractic manipulation of the cervical spine. J Headache Pain. 2006;7:211–213. doi: 10.1007/s10194-006-0308-0. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
26. Marx P, Püschmann H, Haferkamp G, Busche T, Neu J. Manipulative treatment of the cervical spine and stroke. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2009;77:83–90. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1109083. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
27. Gouveia LO, Gastanho P, Ferreira JJ. Safety of chiropractic intervention. A systematic review. Spine. 2009;34:E405–E413. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181a16d63. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
28. Ernst E. The safety of massage therapy. Rheumatology. 2003;42:1101–1106. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keg306. [PubMed] [Cross Ref]
29. Zeppos L, Patman S, Berney S, Adsett JA, Bridson JM, Paratz JD. Physiotherapy in intensive care is safe: an observational study. Aust J Physiother. 2007;53:279–283. [PubMed]

Additional Topics: Neck Pain
Neck pain is a common complaint which can result due to a variety of injuries and/or conditions. According to statistics, automobile accident injuries and whiplash injuries are some of the most prevalent causes for neck pain among the general population. During an auto accident, the sudden impact from the incident can cause the head and neck to jolt abruptly back-and-forth in any direction, damaging the complex structures surrounding the cervical spine. Trauma to the tendons and ligaments, as well as that of other tissues in the neck, can cause neck pain and radiating symptoms throughout the human body.

IMPORTANT TOPIC: EXTRA EXTRA: A Healthier You!
OTHER IMPORTANT TOPICS: EXTRA: Sports Injuries? | Vincent Garcia | Patient | El Paso, TX Chiropractor
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information on this blog site is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters and issues that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card