Can incorporating an exercise program like the Alfredson Protocol help athletes and individuals who have hurt their Achilles tendon find pain relief and healing so they can return to regular physical activities?
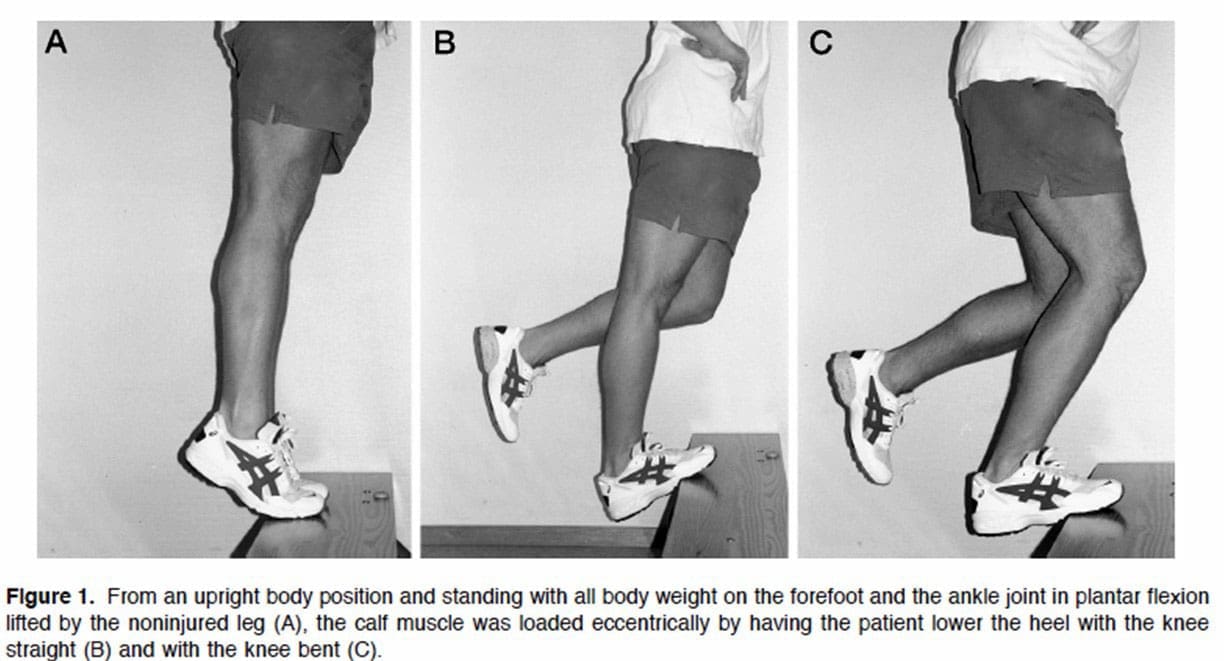
Table of Contents
Exercise Protocol Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis occurs when the tendon at the back of the ankle gets injured. It is common in runners. For individuals who have Achilles tendonitis, walking and running can be painful. You might have to stop engaging in exercise and physical activities like sports. Depending on your job, having the condition may make working harder. Here are a few of the signs and symptoms of the condition:
- Pain in the back of the lower leg, just above the heel.
- Pain with running, jumping, or pointing the toes.
- A small lump on the Achilles tendon just above the heel.
The first line of treatment is to rest and ice the tendon. Anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce pain. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022) Physical therapy can include strengthening exercises, ultrasound heat therapy, and deep massage. Exercises to stretch the nearby muscles will help to gradually increase the stress the tendon can handle, which eventually reduces inflammation and swelling. Stretching and flexibility exercises will help an Achilles tendon heal. (University of Michigan, 2023)
The only way to determine if an individual has injured their Achilles tendon is to see a doctor. If the injury is Achilles tendonitis, a physical therapist may be recommended. A physical therapist can train individuals on the Alfredson protocol, an exercise protocol program for those with Achilles tendonitis (tendinopathy) that research has shown is helpful for those with the condition. The therapist will train on how to exercise to strengthen the tendon. The exercises stretch the Achilles tendon to help it handle forces and stress, known as eccentric loading. (Stevens M., & Tan C. W. 2014)
Inflammation
Tendonitis is inflammation of a tendon. However, studies have shown that the tendon might not be inflamed in those with the condition. When an area of the body is inflamed, inflammatory cells are present. Individuals usually feel pain in the inflamed area. For those with Achilles tendonitis, the tendon will present with pain, but not necessarily because the tendon is inflamed. Under a microscope, researchers examined tissue from the tendons of those with Achilles tendonitis. They did not find inflammatory cells in the tissue. (Stevens M., & Tan C. W. 2014) This means that although individuals felt pain, they were not inflamed. If there are no inflammatory cells in the tendon, this could explain why those with Achilles tendonitis often do not find relief from the anti-inflammatory treatment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Studies have shown that gentle exercise protocol of the tendon are more helpful. However, researchers are not sure why these exercises are so beneficial. (O’Neill S., Watson P. J., & Barry S. 2015)
Eccentric Exercise
A chiropractic physical therapy team can help individuals heal the injury with eccentric loading exercises. Eccentric loading exercises work the muscles and tendons to help them get stronger. Once healing has begun, they can help strengthen the tendon. Individuals start slowly with easy exercises and then work up to harder ones. They will have the patient lengthen or stretch out the muscle. As the patient moves, the muscles and tendons contract or shorten. The Alfredson protocol consists of eccentric loading exercises for the Achilles and the muscles that support it.
Alfredson Protocol
Before exercising, talk to a doctor or physical therapist to know if it’s safe. How to do the Alfredson protocol:
- First, stand on a small step or curb.
- Stand with the balls of your feet on the edge.
- Your heels should hang over the edge.
- Hold onto something for balance.
- Keep the knees straight.
- This will load a muscle part of the Achilles tendon called the gastrocnemius.
- Using both feet, lift the heels and rise onto the balls of the feet.
- Keep the foot with the painful Achilles tendon on the step.
- Lift the non-injured foot off the step.
- Slowly lower down using the injured ankle.
- The heel should move towards the floor.
- The ball of the foot should remain in contact with the edge of the step.
- Return the non-injured foot to the step.
- Repeat the exercise.
Do three sets of 15 reps with the knees straight. Then do the Alfredson protocol again with the knees slightly bent. This will work a muscle called the soleus, which connects to the gastrocnemius. Perform three sets of 15 repetitions. Perform both exercises twice a day. This could be in the morning and in the evening. The Alfredson protocol is most beneficial when done for about 12 weeks. (Stevens M., & Tan C. W. 2014)
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic
The Alfredson exercise protocol can be done at home with a step or raised platform to safely put the feet on. Individuals should consider working with a personal trainer to ensure safety and get the most out of the workouts. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to build optimal health and wellness solutions. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, prevent injury, and help mitigate issues through adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal problems.
Functional Foot Orthotics Achieve Optimal Performance
References
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. OrthoInfo. (2022). Achilles Tendinitis. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/achilles-tendinitis/
University of Michigan. (2023). Achilles Tendon Injury: Physical Therapy and Rehab. https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/tr2261
Stevens, M., & Tan, C. W. (2014). Effectiveness of the Alfredson protocol compared with a lower repetition-volume protocol for midportion Achilles tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial. The Journal of orthopaedic and sports physical therapy, 44(2), 59–67. https://doi.org/10.2519/jospt.2014.4720
O’Neill, S., Watson, P. J., & Barry, S. (2015). WHY ARE ECCENTRIC EXERCISES EFFECTIVE FOR ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY?. International journal of sports physical therapy, 10(4), 552–562.
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information on this blog site is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters and issues that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card


