Table of Contents
Do you feel:
- That eating relieves fatigue?
- Hormone imbalances?
- Aches, pains, and swelling throughout the body?
- Bodily swelling for no reason?
- Inflammation on your body?
If you are experiencing any of these situations, you might be experiencing inflammation, and it might affect your endocrine system.
Inflammation and the Endocrine System
Inflammation is a defense mechanism in the body. The immune system can recognize the damaged cells, irritants, and pathogens that cause harm to the body and began the healing process. When the inflammation turns into chronic inflammation, it can cause several diseases and conditions in the body and can cause harm to an individual.
Inflammation can cause dysfunction when it is in the endocrine system. The endocrine system is a series of glands that produce and secretes hormones that the body needs and uses for a wide range of functions. When the endocrine glands produce hormones, they are sent into the bloodstream to the various tissues in the body. Once they are in the various tissues, the hormone signals the tissues to tell them what they are supposed to do. When the glands do not produce the right amount of hormones, various diseases like inflammation can affect the body.
Inflammation Symptoms and Causes
Two questions are asked concerning the interaction of the endocrine system with inflammation: How does inflammation influences the endocrine system, and does it influences disease? How do hormones influence inflammation and immune cells? A theory had integrated both questions and has recently been demonstrated in the context of chronic inflammation considering a rheumatic disease.
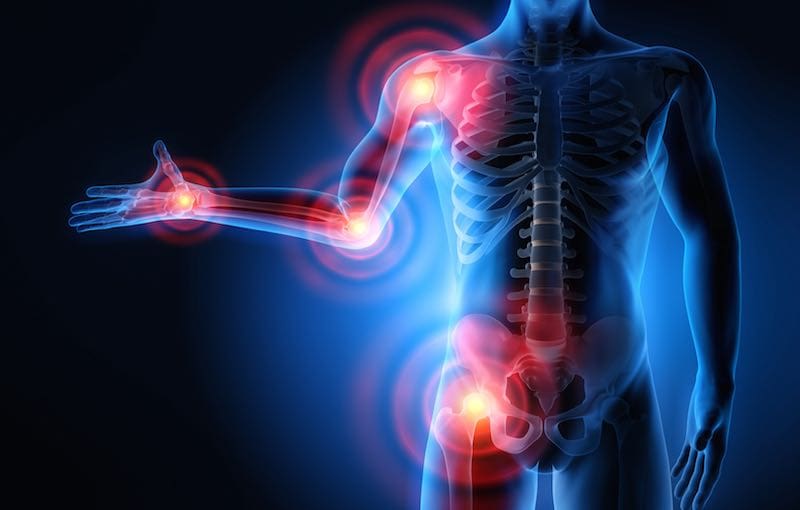
So how does inflammation influence the endocrine system? Inflammation symptoms can vary depending on if it is acute or chronic. The effects of acute inflammation are summed up by the acronym PRISH. They include:
- Pain: The inflamed area is most likely to be painful, especially during and after touching. The chemicals that stimulate the nerve endings are released, making the area more sensitive.
- Redness: This occurs due to the capillaries in the area that is filled with more blood than usual.
- Immobility: There may be some loss of function in the region of the inflammation where the injury has occurred.
- Swelling: A buildup of fluid causes this.
- Heat: Heat is caused by having more blood flow to the affected area and making it warm to the touch.
These acute inflammation signs only apply to an inflammation on the skin. If the inflammation occurs deep inside the body, like the endocrine system and the internal organs, some of the signs may be noticeable. Some internal organs may not have sensory nerve endings nearby; for example, they will not have pain.
With the effects of chronic inflammation, it is long term and can last for several months or even years. The results from chronic inflammation can be from:
- An autoimmune disorder that attacks normal healthy tissue and mistaking it for a pathogen that causes diseases like fibromyalgia.
- An industrial chemical that is exposed to a low level of a particular irritant over a long period.
- Failure to eliminate whatever was causing acute inflammation.
Some of the symptoms of chronic inflammation can be present in different ways. These can include:
- Fatigue
- Mouth sores
- Chest pains
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
- Rash
- Joint pain
When inflammation affects the endocrine system, it can cause the body’s system to be unbalanced, and it can lead to chronic long term illnesses.
With the second question, it is asking how do hormones influence inflammation and the immune system? When the hormone levels are either too high or too low, it can have several effects on a person’s health. The signs and symptoms can depend on hormones that are out of balance.
Inflammation and Hormones
Research has shown that some of the conditions that are affecting the endocrine system can lead to autoimmune disorders. High levels of hormones can lead to hyperthyroidism, Cushing syndrome, and Graves disease. While low levels of hormones can lead to hypothyroidism and Addison disease. When the levels of the hormones are either too high or too low, the body fluctuates from either weight gain or weight loss and disrupting the glucose levels. This can cause a person to get diabetes and obesity.
Obesity is the main risk factor for type 2 diabetes. During the development of obesity, subclinical inflammatory activity in the tissues are activated and involves the metabolism and energy homeostasis. In the body, intracellular serine/threonine kinases are activated in response to those inflammatory factors. They can catalyze the inhibitory phosphorylation of the key proteins of the insulin-signaling pathway, leading to insulin resistance in the body.
Studies have shown that inflammation is a general tissue response to a wide variety of stimuli. When inflammation is not adequately regulated, inflammatory responses may be exaggerated or ineffective, which can lead to immune dysfunction, recurring infections, and tissue damage, both locally and systemically. With various hormones, cytokines, vitamins, metabolites, and neurotransmitters being key meditators of the immune and inflammatory responses to the endocrine system.
Another study shows that aging, chronic psychological stress, and mental illnesses are also accompanied by chronic smoldering inflammation. Chronic smoldering inflammation in humans is already established with elevations of serum levels, leading to an increase in resting metabolic rate.
Conclusion
So inflammation is a double edge sword where it can heal the body but also cause the body harm if it is deep into the internal organs and body systems. With the endocrine system, the levels of the hormones can fluctuate from going too high or too low and affecting the tissues in the body, causing inflammation. When an individual is suffering from chronic inflammation, it can change their lifestyle drastically. Some products are here to help counter the metabolic effects of temporary stress and make sure that the endocrine system is supported as well.
The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, and nervous health issues or functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We use functional health protocols to treat injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We also make copies of supporting research studies available to the board and or the public upon request. To further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900.
References:
Coope, Andressa, et al. “MECHANISMS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY: Metabolic and Inflammatory Pathways on the Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes.” European Journal of Endocrinology, U.S. National Library of Medicine, May 2016, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26646937.
Felman, Adam. “Inflammation: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment.” Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, 24 Nov. 2017, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/248423.php.
Salazar, Luis A., et al. “The Role of Endocrine System in the Inflammatory Process.” Mediators of Inflammation, Hindawi, 29 Sept. 2016, www.hindawi.com/journals/mi/2016/6081752/.
Seladi-Schulman, Jill. “Endocrine System Overview.” Healthline, 22 Apr. 2019, www.healthline.com/health/the-endocrine-system.
Straub, Rainer H. “Interaction of the Endocrine System with Inflammation: a Function of Energy and Volume Regulation.” Arthritis Research & Therapy, BioMed Central, 13 Feb. 2014, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3978663/.
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information on this blog site is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters and issues that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card