Individuals dealing with back pain problems could be suffering from a bulging disc. Could knowing the difference between slipped and herniated disc symptoms help with treatments and finding relief?
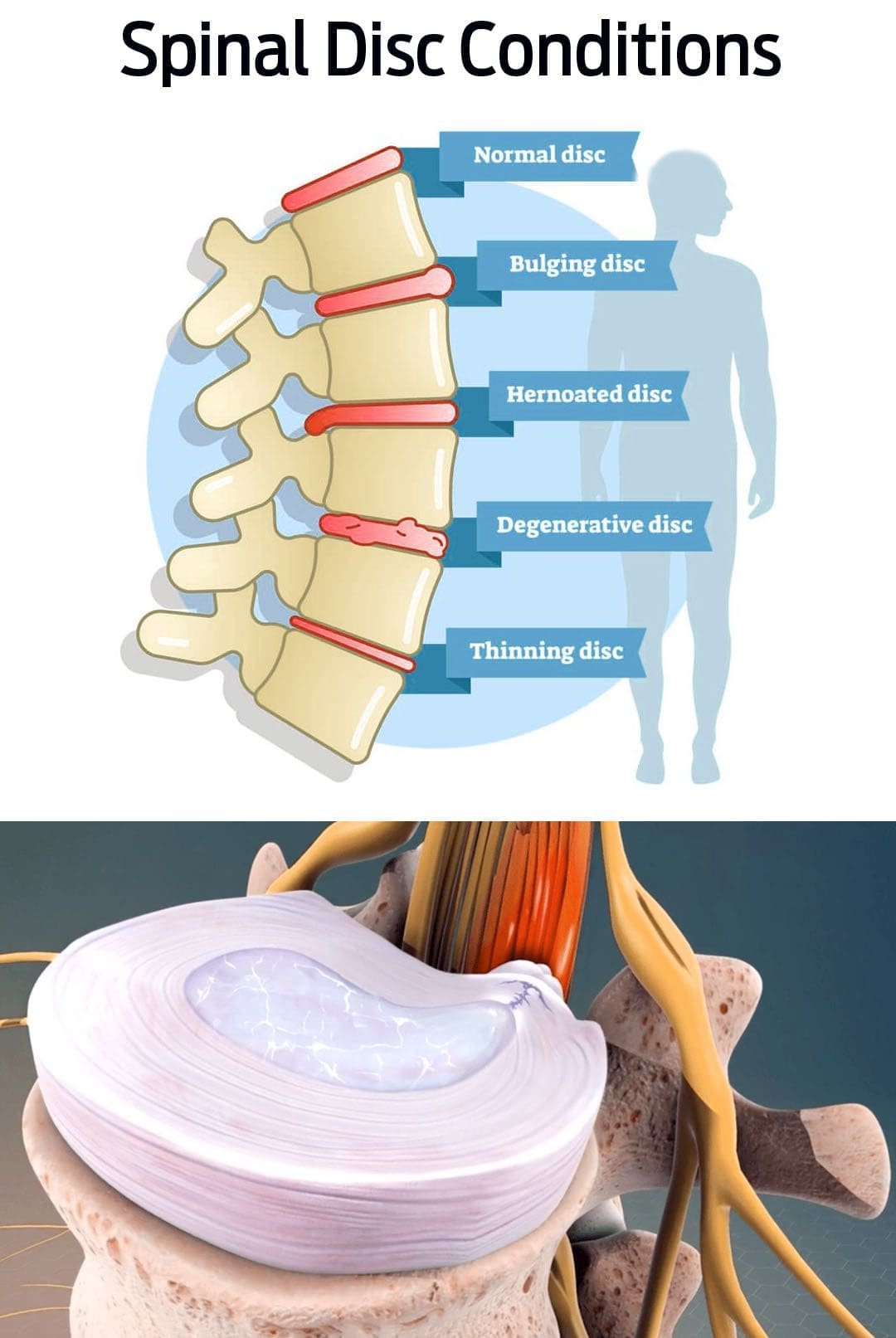
Table of Contents
Bulging Disc Pain
Back pain can become debilitating if not treated properly. A bulging disc is a common cause of cervical, thoracic, and lower back pain symptoms. It happens when one of the fluid-filled cushions between the vertebrae begins to shift out of place. Instead of being aligned with the edges, the disc bulges over. This begins to generate pressure on the nerves causing pain and inflammation.
- Bulging discs are often caused by age, but repetitive movements and/or lifting heavy objects can contribute to the condition.
- Symptoms can resolve on their own, but individuals are recommended to consult with a physical therapist and/or chiropractor to make sure the disc healed properly, otherwise, it can lead to worsening and/or further injuries.
Bulging Disc vs. Herniated Disc
Bulging and herniated discs cause pain symptoms.
- They both can be linked to injuries and degenerative disc disease but are not the same condition. (Penn Medicine. 2018)
- Sometimes the terms bulging and herniated disc are used interchangeably, which can be confusing. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2022)
- Bulging – the intervertebral disc moves out of place but stays intact.
- Herniated – the thick outer layer of the disc ruptures, causing the cushioning gel inside to leak onto the spinal nerves.
Location of Symptoms
- A bulging disc can happen anywhere along the spine.
- However, most occur between the last five vertebrae in the lower back.
- This is the lumbar spine. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2022)
- This is because the lower back is subject to all kinds of pressure and movement with daily activities, increasing the chances of pain and injuries.
- The next most common place is the neck/cervical spine where there are constant movements making it prone to injury and pain symptoms.
Causes
Bulging discs are most often caused by body aging and normal wear and tear. As time goes on the intervertebral discs naturally degenerate, known as degenerative disc disease. This can cause the discs to pull downward, causing them to bulge from their placement. (Penn Medicine. 2018) Factors that can cause or worsen the condition include:
- Practicing unhealthy postures.
- Repetitive motions.
- Lifting heavy objects
- Spinal injuries.
- Medical history of spinal or disc disease in the family.
Treatment
Treating a bulging disc takes time and patience. (American Academy of Neurological Surgeons. 2023)
Examination
Individuals with back pain that interferes with daily functions or has lasted longer than six weeks, should see a healthcare provider for diagnosis. They will order a magnetic resonance imaging scan/MRI, which can show where a disc is protruding. (American Academy of Neurological Surgeons. 2023)
Rest
- For bulging disc pain, resting the back is necessary. However,
- Many patients benefit from a day or two of bed rest. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2022)
- After that, start light activities like walking. Avoid any movements that make your pain worse.
NSAIDs
- NSAID pain medications like Advil, Motrin, or Aleve can keep pain symptoms and inflammation reduced.
- However, this is for short-term use, as the underlying cause still needs to be addressed.
- A healthcare provider will recommend safe dosage and how long these medications should be taken. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2022)
Physical Therapy
- Individuals may be recommended by their healthcare provider for a referral to a physical therapist.
- A physical therapist will address the injury for rehabilitation and introduce strengthening exercises. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2022)
- Chiropractic Adjustments (NIH. 2022)
- Non-surgical spinal decompression
- Traction therapy
- Therapeutic massage
- Muscle Energy Technique
Steroid Injection
- An epidural steroid injection can provide relief for individuals still experiencing symptoms after six weeks.
- A healthcare provider will inject cortisone into the spine to reduce inflammation and pain. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2022)
Surgery
- If conservative treatments don’t work, a healthcare provider may recommend surgery, like a microdiscectomy.
- This procedure uses small incisions to remove all or part of a bulging disc.
- Most individuals with a bulging disc will not require surgery. (American Academy of Neurological Surgeons. 2023)
Inflammation: Integrative Medicine Approach
References
Penn Medicine. (2018) Bulging disc vs. herniated disc: What’s the difference?
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2022) Herniated disk in the lower back.
American Academy of Neurological Surgeons. (2023) Herniated disc.
National Institutes of Health. (2022) Spinal Manipulation: What You Need To Know.
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information on this blog site is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters and issues that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card


